HIV-1 Nef is carried on the surface of extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 39016173
- PMCID: PMC11252832
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12478
HIV-1 Nef is carried on the surface of extracellular vesicles
Abstract
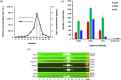
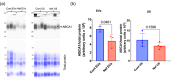
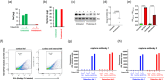
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) serve as pivotal mediators of intercellular communication in both health and disease, delivering biologically active molecules from vesicle-producing cells to recipient cells. In the context of HIV infection, EVs have been shown to carry the viral protein Nef, a key pathogenic factor associated with HIV-related co-morbidities. Despite this recognition, the specific localisation of Nef within the vesicles has remained elusive. This study addresses this critical knowledge gap by investigating Nef-containing EVs. Less than 1% of the total released Nef was associated with EVs; most Nef existed as free protein released by damaged cells. Nevertheless, activity of EV-associated Nef in downregulating the major cholesterol transporter ABCA1, a critical aspect linked to the pathogenic effects of Nef, was comparable to that of free Nef present in the supernatant. Through a series of biochemical and microscopic assays, we demonstrate that the majority of EV-associated Nef molecules are localised on the external surface of the vesicles. This distinctive distribution prompts the consideration of Nef-containing EVs as potential targets for immunotherapeutic interventions aimed at preventing or treating HIV-associated co-morbidities. In conclusion, our results shed light on the localisation and functional activity of Nef within EVs, providing valuable insights for the development of targeted immunotherapies to mitigate the impact of HIV-associated co-morbidities.
Keywords: ELISA; HIV‐1; Nef; extracellular vesicles.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HIV-1 Nef-Induced Secretion of the Proinflammatory Protease TACE into Extracellular Vesicles Is Mediated by Raf-1 and Can Be Suppressed by Clinical Protein Kinase Inhibitors.J Virol. 2021 Apr 12;95(9):e00180-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00180-21. Print 2021 Apr 12. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33597213 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of lipid rafts by extracellular vesicles carrying HIV-1 protein Nef induces redistribution of amyloid precursor protein and Tau, causing neuronal dysfunction.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 18;295(38):13377-13392. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014642. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32732283 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef Protein Affects Cytokine and Extracellular Vesicles Production in the GEN2.2 Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Line.Viruses. 2021 Dec 31;14(1):74. doi: 10.3390/v14010074. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 35062278 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of Nef in the Development of HIV Associated Neurological Disorders.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021 Jun;16(2):238-250. doi: 10.1007/s11481-020-09964-1. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33123948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How HIV Nef Proteins Hijack Membrane Traffic To Promote Infection.J Virol. 2019 Nov 26;93(24):e01322-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01322-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31578291 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aiken, C. , Konner, J. , Landau, N. R. , Lenburg, M. E. , & Trono, D. (1994). Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: Requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane‐proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell, 76, 853–864. - PubMed
-
- Bachurski, D. , Schuldner, M. , Nguyen, P. H. , Malz, A. , Reiners, K. S. , Grenzi, P. C. , Babatz, F. , Schauss, A. C. , Hansen, H. P. , Hallek, M. , & Pogge von Strandmann, E. (2019). Extracellular vesicle measurements with nanoparticle tracking analysis—An accuracy and repeatability comparison between NanoSight NS300 and ZetaView. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 8, 1596016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burdo, T. H. , Lo, J. , Abbara, S. , Wei, J. , DeLelys, M. E. , Preffer, F. , Rosenberg, E. S. , Williams, K. C. , & Grinspoon, S. (2011). Soluble CD163, a novel marker of activated macrophages, is elevated and associated with noncalcified coronary plaque in HIV‐infected patients. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 204, 1227–1236. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

