β-Tocotrienol Decreases PDGF-BB-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells by Inhibiting RhoA and Reducing ROS Production
- PMID: 38931379
- PMCID: PMC11206512
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060712
β-Tocotrienol Decreases PDGF-BB-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells by Inhibiting RhoA and Reducing ROS Production
Abstract
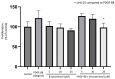
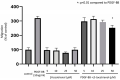
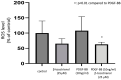
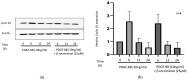
Background: Tocotrienols exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. RhoA, a small GTPase protein, plays a crucial role in regulating contractility in airway smooth muscle (ASM). Previous studies have demonstrated that γ-tocotrienols reduce ASM proliferation and migration by inhibiting the activation of RhoA. In this present study, we investigate the effect of another vitamin E isoform, β-tocotrienols, on human ASM cell proliferation and migration stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB).
Methods: Human ASM cells were pre-treated with β-tocotrienol prior to being stimulated with PDGF-BB to induce ASM cell proliferation and migration. The proliferation and migration of PDGF-BB-induced human ASM cells were assessed using colorimetric and transwell migration assays. The intracellular ROS assay kit was employed to quantify reactive oxygen species (ROS) in human ASM cells. Additionally, we explored the effect of β-tocotrienols on the signaling pathways involved in PDGF-BB-induced ASM proliferation and migration.
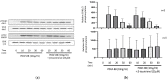
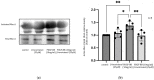
Results: β-tocotrienol inhibited PDGF-BB-induced ASM cell proliferation and migration by reducing RhoA activation and ROS production. However, in this present study, β-tocotrienol did not affect the signaling pathways associated with cyclin D1, phosphorylated Akt1, and ERK1/2.
Conclusions: In conclusion, the inhibition of RhoA activation and ROS production by β-tocotrienol, resulting in the reduction in human ASM proliferation and migration, suggests its potential as a treatment for asthma airway remodeling.
Keywords: ASM; ROS; Rho-A; airway remodeling; asthma; tocotrienol; vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
γ-Tocotrienol reduces human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jun;32:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 May 6. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25956071
-
γ-Tocotrienol Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Contractile Phenotype Expression of Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells.Yonago Acta Med. 2017 Mar 9;60(1):16-23. eCollection 2017 Mar. Yonago Acta Med. 2017. PMID: 28331417 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA/ROCK signaling regulates smooth muscle phenotypic modulation and vascular remodeling via the JNK pathway and vimentin cytoskeleton.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Jul;133:201-212. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.05.011. Epub 2018 May 20. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29791873
-
Gambogic acid induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and cell migration inhibition via suppressing PDGF receptor β tyrosine phosphorylation and Rac1 activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010 Sep 30;17(9):901-13. doi: 10.5551/jat.3491. Epub 2010 Jun 11. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010. PMID: 20543524
-
MicroRNA-638 inhibits human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through targeting cyclin D1 and NOR1.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;234(1):369-381. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26930. Epub 2018 Aug 4. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30076719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GINA From the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) 2023. [(accessed on 8 February 2024)]. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/
-
- Hough K.P., Curtiss M.L., Blain T.J., Liu R.-M., Trevor J., Deshane J.S., Thannickal V.J. Airway Remodeling in Asthma. [(accessed on 8 February 2024)];Front. Med. 2020 7:191. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00191. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2020.00191. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

