Structure and topography of the synaptic V-ATPase-synaptophysin complex
- PMID: 38838737
- PMCID: PMC11269182
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07610-x
Structure and topography of the synaptic V-ATPase-synaptophysin complex
Abstract
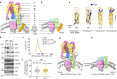
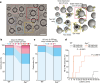
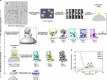
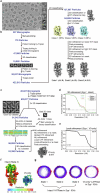
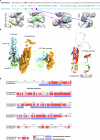
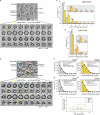
Synaptic vesicles are organelles with a precisely defined protein and lipid composition1,2, yet the molecular mechanisms for the biogenesis of synaptic vesicles are mainly unknown. Here we discovered a well-defined interface between the synaptic vesicle V-ATPase and synaptophysin by in situ cryo-electron tomography and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy of functional synaptic vesicles isolated from mouse brains3. The synaptic vesicle V-ATPase is an ATP-dependent proton pump that establishes the proton gradient across the synaptic vesicle, which in turn drives the uptake of neurotransmitters4,5. Synaptophysin6 and its paralogues synaptoporin7 and synaptogyrin8 belong to a family of abundant synaptic vesicle proteins whose function is still unclear. We performed structural and functional studies of synaptophysin-knockout mice, confirming the identity of synaptophysin as an interaction partner with the V-ATPase. Although there is little change in the conformation of the V-ATPase upon interaction with synaptophysin, the presence of synaptophysin in synaptic vesicles profoundly affects the copy number of V-ATPases. This effect on the topography of synaptic vesicles suggests that synaptophysin assists in their biogenesis. In support of this model, we observed that synaptophysin-knockout mice exhibit severe seizure susceptibility, suggesting an imbalance of neurotransmitter release as a physiological consequence of the absence of synaptophysin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

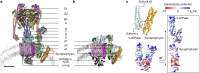




Similar articles
-
High-resolution electron cryomicroscopy of V-ATPase in native synaptic vesicles.Science. 2024 Jul 12;385(6705):168-174. doi: 10.1126/science.adp5577. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Science. 2024. PMID: 38900912
-
Neurotransmitter release: the dark side of the vacuolar-H+ATPase.Biol Cell. 2003 Oct;95(7):453-7. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(03)00075-3. Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14597263 Review.
-
A role for V-ATPase subunits in synaptic vesicle fusion?J Neurochem. 2011 May;117(4):603-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07234.x. Epub 2011 Mar 28. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21375531 Review.
-
The V0 sector of the V-ATPase, synaptobrevin, and synaptophysin are associated on synaptic vesicles in a Triton X-100-resistant, freeze-thawing sensitive, complex.J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 26;271(4):2193-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.4.2193. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8567678
-
Synaptic vesicle alterations in rod photoreceptors of synaptophysin-deficient mice.Neuroscience. 2001;107(1):127-42. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00345-1. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11744253
Cited by
-
Structure of the flotillin complex in a native membrane environment.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 16;121(29):e2409334121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2409334121. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38985763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takamori, S. et al. Molecular anatomy of a trafficking organelle. Cell127, 831–846 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Bodzęta, A., Kahms, M. & Klingauf, J. The presynaptic v-ATPase reversibly disassembles and thereby modulates exocytosis but is not part of the fusion machinery. Cell Rep.20, 1348–1359 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Casey, J. R., Grinstein, S. & Orlowski, J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.11, 50–61 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

