Neurosyphilis with sequential respiratory complications: A case report highlighting diagnostic and treatment challenges
- PMID: 38817409
- PMCID: PMC11138193
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X241256825
Neurosyphilis with sequential respiratory complications: A case report highlighting diagnostic and treatment challenges
Abstract
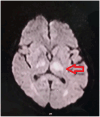
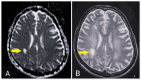
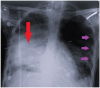
In this case report, we describe the presentation and clinical course of a 25-year-old male with a complex medical history and a fatal outcome due to neurosyphilis. The diagnosis of neurosyphilis-related complications. Neurosyphilis, a variant of tertiary syphilis, is a rare condition but can present with a wide range of neurological symptoms. This makes its diagnosis challenging. The study aims to report and discuss neurosyphilis in a young male, resulting in respiratory complications, and explore the clinical presentation, diagnostic and process, treatment challenges it poses to a tertiary care setup of a third-world country regimen, and the profound significance of this particular case.
Keywords: Neurosyphilis; Treponema pallidum; complications; respiratory.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Malignant syphilis accompanied with neurosyphilis in a malnourished patient: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Aug 26;7(16):2406-2412. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2406. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 31531338 Free PMC article.
-
Neurosyphilis in a non-HIV patient: more than a psychiatric concern.Mcgill J Med. 2008 Jul;11(2):160-3. Mcgill J Med. 2008. PMID: 19148316 Free PMC article.
-
[Neurosyphilis, the great imitator: a diagnostic challenge].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2013;157(30):A6033. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2013. PMID: 23890167 Dutch.
-
[Neurosyphilis: forms of presentation and clinical management].Rev Neurol. 2002 Aug 16-31;35(4):380-6. Rev Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12235572 Review. Spanish.
-
Syphilis: reemergence of an old adversary.Ophthalmology. 2006 Nov;113(11):2074-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.05.048. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Ophthalmology. 2006. PMID: 16935333 Review.
References
-
- Golden MR, Marra CM, Holmes KK. Update on syphilis: resurgence of an old problem. JAMA 2003; 290(11): 1510–1514. - PubMed
-
- Gjestland T. The Oslo study of untreated syphilis, an epidemiologic investigation of the natural course of syphilitic infection based upon a restudy of the Boeck-Bruusgaard material. Acta Derm Venereol 1955; 35: S-34. - PubMed
-
- Tong ML, Liu LL, Zeng YL, et al.. Laboratory findings in neurosyphilis patients with epileptic seizures alone as the initial presenting symptom. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2013; 75(4): 377–380. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

