Role of gut microbiota in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: from pathogenesis to related interventions
- PMID: 38720361
- PMCID: PMC11077873
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05232-5
Role of gut microbiota in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: from pathogenesis to related interventions
Abstract
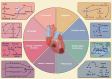
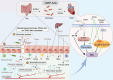
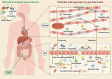
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a broad-spectrum and highly efficient anticancer agent, but its clinical implication is limited by lethal cardiotoxicity. Growing evidences have shown that alterations in intestinal microbial composition and function, namely dysbiosis, are closely linked to the progression of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC) through regulating the gut-microbiota-heart (GMH) axis. The role of gut microbiota and its metabolites in DIC, however, is largely unelucidated. Our review will focus on the potential mechanism between gut microbiota dysbiosis and DIC, so as to provide novel insights into the pathophysiology of DIC. Furthermore, we summarize the underlying interventions of microbial-targeted therapeutics in DIC, encompassing dietary interventions, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), probiotics, antibiotics, and natural phytochemicals. Given the emergence of microbial investigation in DIC, finally we aim to point out a novel direction for future research and clinical intervention of DIC, which may be helpful for the DIC patients.
Keywords: Cardiotoxicity; Doxorubicin; Gut microbiota; Interventions; Metabolites; Pathogenesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Z-ligustilide alleviates atherosclerosis by reconstructing gut microbiota and sustaining gut barrier integrity through activation of cannabinoid receptor 2.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156117. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156117. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39426255
-
Allogenic faecal microbiota transplantation for antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in critically ill patients (FEBATRICE)-Study protocol for a multi-centre randomised controlled trial (phase II).PLoS One. 2024 Dec 27;19(12):e0310180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310180. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39729440 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiome and Alzheimer's disease: What we know and what remains to be explored.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Dec;102:102570. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102570. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39486524 Review.
-
Characteristic alterations of gut microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with chronic tinnitus: a multi-omics analysis.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jan 7;13(1):e0187824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01878-24. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39555931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life years for 29 Cancer groups from 2010 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(3):420–44. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.6987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Munoz D, et al. 2016 ESC position paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: the Task Force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2016;37(36):2768–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82172574/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81871231/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZR2020MH016/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR202209280042/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- YJKT202171/Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

