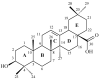
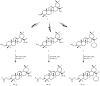
Acylation of Oleanolic Acid Oximes Effectively Improves Cytotoxic Activity in In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 38258097
- PMCID: PMC10819243
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010086
Acylation of Oleanolic Acid Oximes Effectively Improves Cytotoxic Activity in In Vitro Studies
Abstract
(1) Background: The aim of the presented work was to obtain a set of oleanolic acid derivatives with a high level of anticancer activity and a low level of toxicity by applying an economic method. Three types of oleanolic acid derivatives were obtained: (i) derivatives of methyl oleanonate oxime, (ii) derivatives of methyl oleanonate oxime with an additional 11-oxo function, and (iii) derivatives of morpholide of oleanonic acid oxime. (2) Methods: The above oximes were acylated with aliphatic or aromatic carboxylic acid. The newly obtained compounds were subjected to ADMETox analysis and were also tested for cytotoxicity activity on the HeLa, KB, MCF-7, A-549, and HDF cell lines with the MTT assay. (3) Results: Among the tested acylated oximes of oleanolic acid, some derivatives, particularly those with two nitro groups attached to the aromatic ring, proved to be the most potent cytotoxic agents. These triterpene derivatives significantly inhibited the growth of the HeLa, KB, MCF-7, and A-549 cancer cell lines in micromolar concentrations. (4) Conclusions: The introduction of different moieties, particularly the 3,5-dinitro group, resulted in the synthesis of highly potent cytotoxic agents with favorable SI and ADMETox parameters.
Keywords: ADMETox; SAR; acylated oximes; cytotoxic activity; oleanolic acid; oximes; triterpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oleanolic Acid Dimers with Potential Application in Medicine-Design, Synthesis, Physico-Chemical Characteristics, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6989. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136989. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000101 Free PMC article.
-
HYBRIDS OF OLEANOLIC ACID WITH NORBORNENE-2,3-DICARBOXIMIDE-N- CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AS POTENTIAL ANTICANCER AGENTS.Acta Pol Pharm. 2017 May;74(3):827-835. Acta Pol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 29513952
-
Oleanolic Acid A-lactams Inhibit the Growth of HeLa, KB, MCF-7 and Hep-G2 Cancer Cell Lines at Micromolar Concentrations.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016;16(5):579-92. doi: 10.2174/1871520615666150907095756. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26343139
-
Recent advances in synthesis and biological activity of triterpenic acylated oximes.Phytochem Rev. 2015;14(2):203-231. doi: 10.1007/s11101-014-9353-5. Epub 2014 Apr 11. Phytochem Rev. 2015. PMID: 25859175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Cancer Potential of Synthetic Oleanolic Acid Derivatives and Their Conjugates with NSAIDs.Molecules. 2021 Aug 16;26(16):4957. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164957. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oleanolic Acid Dimers with Potential Application in Medicine-Design, Synthesis, Physico-Chemical Characteristics, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6989. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136989. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000101 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Oleanolic Acid Dimers-Cytostatic and Antioxidant Activities, Molecular Docking, and ADMETox Profile.Molecules. 2024 Jul 31;29(15):3623. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153623. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nirmala M.J., Samundeeswari A., Sankar P.D. Natural plant resources in anti-cancer therapy—A review. Res. Plant Biol. 2011;1:1–14.
-
- Patočka J. Biologically active pentacyclic triterpenes and their current medicine. J. Appl. Biomed. 2003;1:7–12. doi: 10.32725/jab.2003.002. - DOI
-
- Yeung M.F., Che C.T. A review on the presence of oleanolic acid in natural products. Nat. Proda Medica. 2009;2:77–290.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous