VLDL Biogenesis and Secretion: It Takes a Village
- PMID: 38236950
- PMCID: PMC11284300
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323284
VLDL Biogenesis and Secretion: It Takes a Village
Abstract
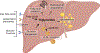
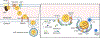
The production and secretion of VLDLs (very-low-density lipoproteins) by hepatocytes has a direct impact on liver fat content, as well as the concentrations of cholesterol and triglycerides in the circulation and thus affects both liver and cardiovascular health, respectively. Importantly, insulin resistance, excess caloric intake, and lack of physical activity are associated with overproduction of VLDL, hepatic steatosis, and increased plasma levels of atherogenic lipoproteins. Cholesterol and triglycerides in remnant particles generated by VLDL lipolysis are risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and have garnered increasing attention over the last few decades. Presently, however, increased risk of atherosclerosis is not the only concern when considering today's cardiometabolic patients, as they often also experience hepatic steatosis, a prevalent disorder that can progress to steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. This duality of metabolic risk highlights the importance of understanding the molecular regulation of the biogenesis of VLDL, the lipoprotein that transports triglycerides and cholesterol out of the liver. Fortunately, there has been a resurgence of interest in the intracellular assembly, trafficking, degradation, and secretion of VLDL by hepatocytes, which has led to many exciting new molecular insights that are the topic of this review. Increasing our understanding of the biology of this pathway will aid to the identification of novel therapeutic targets to improve both the cardiovascular and the hepatic health of cardiometabolic patients. This review focuses, for the first time, on this duality.
Keywords: apolipoprotein B; dyslipidemia; fatty liver; hepatocytes; triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

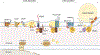
Similar articles
-
Erratum: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs.J Vis Exp. 2023 May 26;(195). doi: 10.3791/6561. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37235796
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Gadolinium Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2023 Jul 3. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Jul 3. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 29494094 Free Books & Documents.
-
Gallium Scan.2022 Dec 26. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2022 Dec 26. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 33620825 Free Books & Documents.
-
Cholesterol Lowering Drugs.2024 Feb 12. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. 2024 Feb 12. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. PMID: 27809434 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
CLCC1 promotes hepatic neutral lipid flux and nuclear pore complex assembly.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 8:2024.06.07.597858. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.07.597858. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38895340 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Rab2A-mediated Golgi-lipid droplet interactions support very-low-density lipoprotein secretion in hepatocytes.EMBO J. 2024 Dec;43(24):6383-6409. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00288-x. Epub 2024 Nov 4. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39496977 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the mysteries of VLDL: exploring its production, intracellular trafficking, and metabolism as therapeutic targets.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jan 12;23(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01993-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38216994 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Mitochondrial and Peroxisomal Metabolism in Female Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 19;25(20):11237. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011237. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of fat-inducing transcript 2 in endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis and lipoprotein biogenesis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2024 Oct 1;35(5):248-252. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000943. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2024. PMID: 39172716 Review.
References
-
- Ginsberg HN, Packard CJ, Chapman MJ, Borén J, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Averna M, Ference BA, Gaudet D, Hegele RA, Kersten S, et al. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants: metabolic insights, role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and emerging therapeutic strategies—a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:4791–4806. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rader DJ, Kastelein JJP. Lomitapide and mipomersen: Two first-in-class drugs for reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. 2014;129:1022–1032. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

