Programmable synthetic receptors: the next-generation of cell and gene therapies
- PMID: 38167329
- PMCID: PMC10761793
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01680-5
Programmable synthetic receptors: the next-generation of cell and gene therapies
Abstract
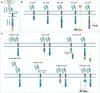
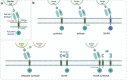
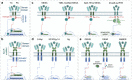
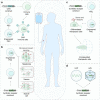
Cell and gene therapies hold tremendous promise for treating a range of difficult-to-treat diseases. However, concerns over the safety and efficacy require to be further addressed in order to realize their full potential. Synthetic receptors, a synthetic biology tool that can precisely control the function of therapeutic cells and genetic modules, have been rapidly developed and applied as a powerful solution. Delicately designed and engineered, they can be applied to finetune the therapeutic activities, i.e., to regulate production of dosed, bioactive payloads by sensing and processing user-defined signals or biomarkers. This review provides an overview of diverse synthetic receptor systems being used to reprogram therapeutic cells and their wide applications in biomedical research. With a special focus on four synthetic receptor systems at the forefront, including chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) and synthetic Notch (synNotch) receptors, we address the generalized strategies to design, construct and improve synthetic receptors. Meanwhile, we also highlight the expanding landscape of therapeutic applications of the synthetic receptor systems as well as current challenges in their clinical translation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. As an editorial board member of the journal, Q.Z. did not participate in any reviewing process of this review article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modular design of synthetic receptors for programmed gene regulation in cell therapies.Cell. 2022 Apr 14;185(8):1431-1443.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.023. Cell. 2022. PMID: 35427499 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering T Cells with Customized Therapeutic Response Programs Using Synthetic Notch Receptors.Cell. 2016 Oct 6;167(2):419-432.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27693353 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational covalent assembly of CAR and synNotch receptors for programmable antigen targeting.Nat Commun. 2023 May 9;14(1):2463. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37863-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37160880 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning CARs: recent advances in modulating chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell activity for improved safety, efficacy, and flexibility.J Transl Med. 2023 Mar 15;21(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04041-6. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36922828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy, Applicability, and Safety of Genetically Engineered Immune Cells.Crit Rev Immunol. 2021;41(1):41-67. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2021037437. Crit Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33822524 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosimilars in the Era of Artificial Intelligence-International Regulations and the Use in Oncological Treatments.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 10;17(7):925. doi: 10.3390/ph17070925. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The next frontier in immunotherapy: potential and challenges of CAR-macrophages.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Aug 5;13(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00549-9. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39103972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positions of cysteine residues reveal local clusters and hidden relationships to Sequons and Transmembrane domains in Human proteins.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 29;14(1):25886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77056-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468182 Free PMC article.
-
A Roadmap of CAR-T-Cell Therapy in Glioblastoma: Challenges and Future Perspectives.Cells. 2024 Apr 23;13(9):726. doi: 10.3390/cells13090726. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38727262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31621004/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31621004/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32201193/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2022M713133/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

