Comparative genome-wide characterization of salt responsive micro RNA and their targets through integrated small RNA and de novo transcriptome profiling in sugarcane and its wild relative Erianthus arundinaceus
- PMID: 38162015
- PMCID: PMC10756875
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03867-7
Comparative genome-wide characterization of salt responsive micro RNA and their targets through integrated small RNA and de novo transcriptome profiling in sugarcane and its wild relative Erianthus arundinaceus
Abstract
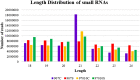
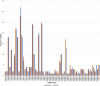
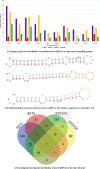
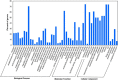
Soil salinity and saline irrigation water are major constraints in sugarcane affecting the production of cane and sugar yield. To understand the salinity induced responses and to identify novel genomic resources, integrated de novo transcriptome and small RNA sequencing in sugarcane wild relative, Erianthus arundinaceus salt tolerant accession IND 99-907 and salt-sensitive sugarcane genotype Co 97010 were performed. A total of 362 known miRNAs belonging to 62 families and 353 miRNAs belonging to 63 families were abundant in IND 99-907 and Co 97010 respectively. The miRNA families such as miR156, miR160, miR166, miR167, miR169, miR171, miR395, miR399, miR437 and miR5568 were the most abundant with more than ten members in both genotypes. The differential expression analysis of miRNA reveals that 221 known miRNAs belonging to 48 families and 130 known miRNAs belonging to 42 families were differentially expressed in IND 99-907 and Co 97010 respectively. A total of 12,693 and 7982 miRNA targets against the monoploid mosaic genome and a total of 15,031 and 12,152 miRNA targets against the de novo transcriptome were identified for differentially expressed known miRNAs of IND 99-907 and Co 97010 respectively. The gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the miRNA targets revealed that 24, 12 and 14 enriched GO terms (FDR < 0.05) for biological process, molecular function and cellular component respectively. These miRNAs have many targets that associated in regulation of biotic and abiotic stresses. Thus, the genomic resources generated through this study are useful for sugarcane crop improvement through biotechnological and advanced breeding approaches.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03867-7.
Keywords: Salinity; Small RNA; Sugarcane; Transcriptome; miRNA; miRNA targets.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Unveiling Salt Tolerance Mechanisms and Hub Genes in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Through Transcriptomic and WGCNA Analysis.Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 8;13(22):3141. doi: 10.3390/plants13223141. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39599350 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of hub mRNA, lncRNA and miRNA, and associated ceRNA networks implicated in cobia (Rachycentron canadum) scales under hypoosmotic adaption.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2025 Mar;53:101353. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2024.101353. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 39586219
References
-
- Andrews S (2015) FASTQC A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. In: Babraham Inst. https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/. Accessed Dec 2021
-
- Auger A, Galarneau L, Altaf M, Nourani A, Doyon Y, Utley RT, Cronier D, Allard S, Cote J. Eaf1 is the platform for NuA4 molecular assembly that evolutionarily links chromatin acetylation to ATP-dependent exchange of histone H2A variants. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:2257–2270. doi: 10.1128/mcb.01755-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Augustine SM, Narayan JA, Syamaladevi DP, Appunu C, Chakravarthi M, Ravichandran V, Subramonian N. Erianthus arundinaceus HSP70 (EaHSP70) overexpression increases drought and salinity tolerance in sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid) Plant Sci. 2015;232:23–34. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

