Spontaneous p53 activation in middle-aged C57BL/6 mice mitigates the lifespan-extending adaptive response induced by low-dose ionizing radiation
- PMID: 37935713
- PMCID: PMC10630390
- DOI: 10.1038/s41514-023-00123-3
Spontaneous p53 activation in middle-aged C57BL/6 mice mitigates the lifespan-extending adaptive response induced by low-dose ionizing radiation
Abstract
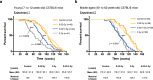
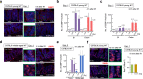
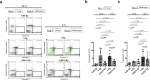
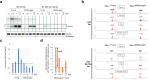
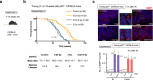
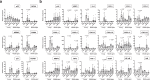
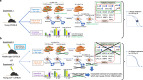
Understanding the biological effects of low-dose (<100 mGy) ionizing radiation (LDR) is technically challenging. We investigated age-dependent LDR effects using adaptive response experiments in young (7-to 12-week-old) and middle-aged (40-to 62-week-old) C57BL/6 mice. Compared with 3 Gy irradiation, 0.02 Gy preirradiation followed by 3 Gy irradiation prolonged life in young mice but not middle-aged mice. Preirradiation also suppressed irradiation-induced 53BP1 repair foci in the small intestines, splenic apoptosis, and p53 activity in young mice but not middle-aged mice. Young p53+/- C57BL/6 mice did not show these adaptive responses, indicating that insufficient p53 function in young mice mitigated the adaptive responses. Interestingly, p53 activation in middle-aged mice spontaneously became approximately 4.5-fold greater than that in young mice, possibly masking LDR stresses. Furthermore, adaptive responses in young mice, but not in middle-aged mice, suppressed some senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors (IL-6, CCL2, CCL5, CXCL1). Thus, LDR-induced adaptive responses associated with specific SASP factors may be attenuated by a combination of reduced DNA damage sensor/transducer function and chronic p53 activation in middle-aged mice.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modification of immune response by low dose ionizing radiation: role of apoptosis.Immunol Lett. 1999 Jun 1;68(2-3):237-45. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(99)00074-7. Immunol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10424426
-
Senescence-associated secretory phenotype and activation of NF-κB in splenocytes of old mice exposed to irradiation at a young age.Dev Comp Immunol. 2021 Sep;122:104124. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2021.104124. Epub 2021 May 8. Dev Comp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33974965
-
p53-mediated metabolic response to low doses of ionizing radiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(6):934-940. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.2142983. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 36357962 Review.
-
Long Bones Exhibit Adaptive Responses to Chronic Low-Dose-Rate Ionizing Radiation despite its Lifespan-Shortening and Carcinogenic Effects on C57BL/6 Mice.JBMR Plus. 2022 Dec 3;6(12):e10688. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10688. eCollection 2022 Dec. JBMR Plus. 2022. PMID: 36530184 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic basis of tissue responses to ionizing radiation.Br J Radiol. 2007 Sep;80 Spec No 1:S2-6. doi: 10.1259/bjr/60507340. Br J Radiol. 2007. PMID: 17704322 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut aging: A wane from the normal to repercussion and gerotherapeutic strategies.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 12;10(19):e37883. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37883. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39381110 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
