Claudin-23 reshapes epithelial tight junction architecture to regulate barrier function
- PMID: 37798277
- PMCID: PMC10556055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41999-9
Claudin-23 reshapes epithelial tight junction architecture to regulate barrier function
Abstract
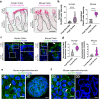
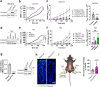
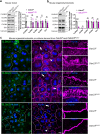
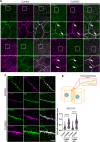
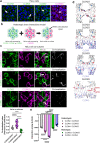
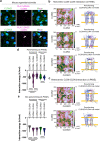
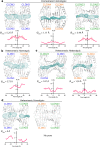
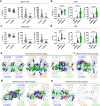
Claudin family tight junction proteins form charge- and size-selective paracellular channels that regulate epithelial barrier function. In the gastrointestinal tract, barrier heterogeneity is attributed to differential claudin expression. Here, we show that claudin-23 (CLDN23) is enriched in luminal intestinal epithelial cells where it strengthens the epithelial barrier. Complementary approaches reveal that CLDN23 regulates paracellular ion and macromolecule permeability by associating with CLDN3 and CLDN4 and regulating their distribution in tight junctions. Computational modeling suggests that CLDN23 forms heteromeric and heterotypic complexes with CLDN3 and CLDN4 that have unique pore architecture and overall net charge. These computational simulation analyses further suggest that pore properties are interaction-dependent, since differently organized complexes with the same claudin stoichiometry form pores with unique architecture. Our findings provide insight into tight junction organization and propose a model whereby different claudins combine to form multiple distinct complexes that modify epithelial barrier function by altering tight junction structure.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computational Modeling of Claudin Structure and Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 23;21(3):742. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030742. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31979311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly of Tight Junction Strands: Claudin-10b and Claudin-3 Form Homo-Tetrameric Building Blocks that Polymerise in a Channel-Independent Manner.J Mol Biol. 2020 Mar 27;432(7):2405-2427. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.02.034. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32142789
-
Ruffles and spikes: Control of tight junction morphology and permeability by claudins.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Sep 1;1862(9):183339. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183339. Epub 2020 May 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32389670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic modeling of the tight junction pore pathway.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Jun;1397(1):209-218. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13374. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017. PMID: 28605031 Free PMC article.
-
Tight junction channel regulation by interclaudin interference.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 30;13(1):3780. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31587-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35773259 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gut aging: A wane from the normal to repercussion and gerotherapeutic strategies.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 12;10(19):e37883. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37883. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39381110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 1 diabetes human enteroid studies reveal major changes in the intestinal epithelial compartment.Sci Rep. 2024 May 24;14(1):11911. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62282-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38789719 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Models of Claudin Assembly in Tight Junctions and Strand Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 16;25(6):3364. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063364. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Claudins in Cancer: A Current and Future Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 24;25(9):4634. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094634. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanostructure-Mediated Transport of Therapeutics through Epithelial Barriers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7098. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137098. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

