cGAS-STING signaling pathway in intestinal homeostasis and diseases
- PMID: 37781354
- PMCID: PMC10538549
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1239142
cGAS-STING signaling pathway in intestinal homeostasis and diseases
Abstract
The intestinal mucosa is constantly exposed to commensal microbes, opportunistic pathogens, toxins, luminal components and other environmental stimuli. The intestinal mucosa consists of multiple differentiated cellular and extracellular components that form a critical barrier, but is also equipped for efficient absorption of nutrients. Combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors are known as critical components involved in the pathogenesis of intestinal diseases. The innate immune system plays a critical role in the recognition and elimination of potential threats by detecting pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). This host defense is facilitated by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), in which the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) pathway has gained attention due to its role in sensing host and foreign double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) as well as cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) produced by bacteria. Upon binding with dsDNA, cGAS converts ATP and GTP to cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP), which binds to STING and activates TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), inducing type I interferon (IFN) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokines, which have diverse effects on innate and adaptive immune cells and intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). However, opposite perspectives exist regarding the role of the cGAS-STING pathway in different intestinal diseases. Activation of cGAS-STING signaling is associated with worse clinical outcomes in inflammation-associated diseases, while it also plays a critical role in protection against tumorigenesis and certain infections. Therefore, understanding the context-dependent mechanisms of the cGAS-STING pathway in the physiopathology of the intestinal mucosa is crucial for developing therapeutic strategies targeting the cGAS-STING pathway. This review aims to provide insight into recent findings of the protective and detrimental roles of the cGAS-STING pathway in intestinal diseases.
Keywords: STING; cGAS; colorectal cancer; inflammatory bowel diseases; intestinal infections; intestinal ischemia/reperfusion.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Wang, Peugnet-González, Parada-Venegas, Dijkstra and Faber.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

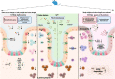
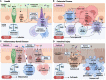
Similar articles
-
The cGAS-STING signaling in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: Future novel target option for pharmacotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):50-75. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 May 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A STING to inflammation and autoimmunity.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Jul;106(1):171-185. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4MIR1018-397RR. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30990921 Review.
-
The role of cGAS-STING signalling in liver diseases.JHEP Rep. 2021 Jun 24;3(5):100324. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100324. eCollection 2021 Oct. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage-triggered activation of cGAS-STING pathway induces apoptosis in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells.Mol Immunol. 2021 Mar;131:180-190. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.12.037. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33423764
-
African Swine Fever Virus Armenia/07 Virulent Strain Controls Interferon Beta Production through the cGAS-STING Pathway.J Virol. 2019 May 29;93(12):e02298-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02298-18. Print 2019 Jun 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30918080 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A molecular subtyping associated with the cGAS-STING pathway provides novel perspectives on the treatment of ulcerative colitis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 3;14(1):12683. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63695-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38831059 Free PMC article.
-
Gut aging: A wane from the normal to repercussion and gerotherapeutic strategies.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 12;10(19):e37883. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37883. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39381110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focus on the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway in Sepsis and Its Inflammatory Regulatory Effects.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun 5;17:3629-3639. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S465978. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38855170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria: a breakthrough in combating rheumatoid arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 5;11:1439182. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1439182. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39161412 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cGAS in epithelial dysregulation in inflammatory bowel disease and gastrointestinal malignancies.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1409683. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1409683. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39050748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

