Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity, Oropharynx, and Larynx: A Scoping Review of Treatment Guidelines Worldwide
- PMID: 37686681
- PMCID: PMC10486835
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15174405
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity, Oropharynx, and Larynx: A Scoping Review of Treatment Guidelines Worldwide
Abstract
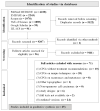
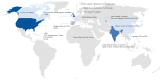
Head and neck cancer (HNC) treatments have been based on single or multimodal therapies with surgery, radiotherapy (RT), chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. However, treatment recommendations among countries may differ due to technological/human resources and usual local practices. This scoping review aims to identify, compare, and map the clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) for treating squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the oral cavity, oropharynx, and larynx worldwide. A search strategy on global CPGs for HNC was performed by using five electronic databases and grey literature. CPGs were selected for inclusion using EndNote-20 and Rayyan online software. No language or publication date restrictions were applied. The results were analyzed descriptively considering the most updated CPG version. In total, 25 CPGs covering the head and neck region (10), the larynx (7), the oral cavity (5), and the oropharynx (3), were found in 13 geographical regions, and 19 were developed by medical societies from 1996 to 2023. Surgery and RT remain the main modalities for early-stage HNC, with surgery preferred in low-resource countries, and RT in selected cases, especially in the larynx/oropharynx aiming to achieve a cure with organ preservation. Human papillomavirus infection for oropharyngeal SCC is not tested in some Asian countries and there is still no consensus to treat p16-positive cases differently from p16-negative. Recommendations for larynx preservation vary according to facilities in each country, however, individualized choice is emphasized. Inequality across countries/continents is evident, with a similar pattern of recommendations among developed as well as developing ones. No CPGs were found in Latin America as well as Oceania countries, where the incidence of HNC is high and limitations of access to treatment may be encountered.
Keywords: cancer treatment; guidelines; head and neck cancer; larynx cancer; oral cancer; oropharynx cancer; scoping review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this work. Where authors are identified as personnel of the International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization, the authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this article and they do not necessarily represent the decisions, policies, or views of the International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Latin American Consensus on the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer.JCO Glob Oncol. 2024 Apr;10:e2300343. doi: 10.1200/GO.23.00343. JCO Glob Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38603656 Review.
-
International trends in head and neck cancer incidence rates: differences by country, sex and anatomic site.Oral Oncol. 2014 May;50(5):387-403. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.01.016. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Oral Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24530208
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
DAHANCA 28: A phase I/II feasibility study of hyperfractionated, accelerated radiotherapy with concomitant cisplatin and nimorazole (HART-CN) for patients with locally advanced, HPV/p16-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx, hypopharynx, larynx and oral cavity.Radiother Oncol. 2020 Jul;148:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.03.025. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Radiother Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32335364 Clinical Trial.
-
Minimally invasive surgery versus radiotherapy/chemoradiotherapy for small-volume primary oropharyngeal carcinoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Dec 11;12(12):CD010963. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010963.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27943254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation Dose-Induced Carotid Artery Stenosis and Brain Necrosis in Head and Neck Cancer-A Real World Cohort Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 27;16(17):2982. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172982. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272840 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Treatment on Quality of Life in Oropharyngeal Cancer Survivors: A 3-Year Prospective Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;16(15):2724. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152724. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123452 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition in HNSCC: is it a matter for oncologists? The role of multidisciplinary team-a narrative literature review.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 3;14:1430845. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1430845. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39022585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Current Evidence and Innovative Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 16;16(10):1905. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101905. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting histone deacetylases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.J Transl Med. 2024 May 3;22(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05169-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38702756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amin M.B., Greene F.L., Edge S.B., Compton C.C., Gershenwald J.E., Brookland R.K., Meyer L., Gress D.M., Byrd D.R., Winchester D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017;67:93–99. doi: 10.3322/caac.21388. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pfister D.G., Spencer S., Adelstein D., Adkins D., Anzai Y., Brizel D.M., Bruce J.Y., Busse P.M., Caudell J.J., Cmelak A.J., et al. Head and Neck Cancers, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020;18:873–898. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

