Endothelial Glycocalyx Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Targeted Therapy
- PMID: 37674786
- PMCID: PMC10480029
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6685251
Endothelial Glycocalyx Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Targeted Therapy
Abstract
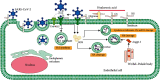
This review aims at summarizing state-of-the-art knowledge on glycocalyx and SARS-CoV-2. The endothelial glycocalyx is a dynamic grid overlying the surface of the endothelial cell (EC) lumen and consists of membrane-bound proteoglycans and glycoproteins. The role of glycocalyx has been determined in the regulation of EC permeability, adhesion, and coagulation. SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to β-coronavirus that causes the outbreak and the pandemic of COVID-19. Through the respiratory tract, SARS-CoV-2 enters blood circulation and interacts with ECs possessing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Intact glycolyx prevents SARS-CoV-2 invasion of ECs. When the glycocalyx is incomplete, virus spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds with ACE2 and enters ECs for replication. In addition, cytokine storm targets glycocalyx, leading to subsequent coagulation disorder. Therefore, it is intriguing to develop a novel treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection through the maintenance of the integrity of glycocalyx. This review aims to summarize state-of-the-art knowledge of glycocalyx and its potential function in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Copyright © 2023 Bingxuan Lv et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial glycocalyx shields the interaction of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with ACE2 receptors.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 9;11(1):12157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91231-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34108510 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin prevents in vitro glycocalyx shedding induced by plasma from COVID-19 patients.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 1;276:119376. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119376. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33781826 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant ACE2 Expression Is Required for SARS-CoV-2 To Infect Primary Human Endothelial Cells and Induce Inflammatory and Procoagulative Responses.mBio. 2020 Dec 11;11(6):e03185-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03185-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33310781 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell dysfunction, coagulation, and angiogenesis in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Microvasc Res. 2021 Sep;137:104188. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104188. Epub 2021 May 20. Microvasc Res. 2021. PMID: 34022205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: A Potential Target to Prevent COVID-19?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 22;12:725967. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.725967. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutual Inhibition of Antithrombin III and SARS-CoV-2 Cellular Attachment to Syndecans: Implications for COVID-19 Treatment and Vaccination.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7534. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147534. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lipowsky H. H. Role of the glycocalyx as a barrier to leukocyte-endothelium adhesion. In: Fu B., Wright N., editors. Molecular, Cellular, and Tissue Engineering of the Vascular System . Vol. 1097. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2018. pp. 51–68. (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology). - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

