High expression of HSP60 and survivin predicts poor prognosis for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients
- PMID: 37661276
- PMCID: PMC10476324
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-03311-5
High expression of HSP60 and survivin predicts poor prognosis for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients
Abstract
Background: HSP60 is a heat shock proteins (HSPs) family member and help mitochondrial protein to fold correctly. Survivin is one of the inhibitors of apoptosis protein family member, which plays a significant part in cancer progression. They were capable of forming HSP60-survivin complexes and involved in the development of various tumors.
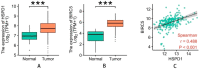
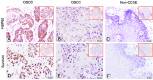
Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database demonstrated that HSP60 and survivin and their correlation on mRNA expression level with OSCC patients. Besides, expression of HSP60 and survivin proteins was studied utilizing immunohistochemistry in tissue microarrays (TMA) in OSCC and in adjacent non-cancerous squamous epithelium (Non-CCSE) tissues.
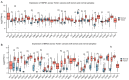
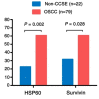
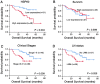
Results: Significantly increased levels of HSP60 and survivin in most cancers compared to normal tissue by pan-cancer analysis. HSP60 and survivin proved a significantly increased expression in OSCC samples compared to Non-CCSE both on mRNA and protein (both P < 0.05). Additionally, elevated HSP60 displayed a positive correlation with survivin in terms of mRNA and protein expression levels (all P < 0.001). Patients with OSCC who had advanced clinical stage or lymph node metastasis (LNM) showed higher HSP60 expression (P = 0.004, P = 0.006, respectively). Higher levels of the proteins HSP60 and survivin were significantly inversely correlated relationship with OSCC patients' overall survival rates in multivariate survival analysis (P = 0.018, P = 0.040). From the above results, overexpression of HSP60 and survivin protein may serve as independent biomarkers predicting poor prognosis in OSCC.
Conclusions: Elevated HSP60 and survivin might be served as novel poor prognosis biomarkers for surgically resected OSCC patients.
Keywords: Biomarker; HSP60; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Prognosis; Survivin.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of survivin in oral squamous cell carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and chemoresistance.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010 Oct;110(4):484-91. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.04.009. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010. PMID: 20868995
-
Upregulation of Synuclein-γ and Snai1 Contributes to Poor Clinical Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 7;2022:6534626. doi: 10.1155/2022/6534626. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35434126 Free PMC article.
-
FLOT-2 is an independent prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):8236-43. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339392 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of survivin as a prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2010 May;39(5):368-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2009.00844.x. Epub 2009 Dec 29. J Oral Pathol Med. 2010. PMID: 20050981
-
Impact of lymphovascular invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2021 Mar;131(3):319-328.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2020.10.026. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33309267 Review.
Cited by
-
MiRNAs in Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Plasma of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Patients: A Proof-of-Concept Study.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 22;13(9):743. doi: 10.3390/biology13090743. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336170 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Response and Heat Shock Proteins: Current Understanding and Future Opportunities in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 10;25(8):4209. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084209. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Microenvironment: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;15(23):5600. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235600. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSPD1 Supports Osteosarcoma Progression through Stabilizing ATP5A1 and thus Activation of AKT/mTOR Signaling.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;20(13):5162-5190. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.100015. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39430254 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathologic significance of heat shock protein 60 as a survival predictor in breast carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 19;14:1415762. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1415762. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39224812 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

