Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern potentially expand host range to chickens: insights from AXL, NRP1 and ACE2 receptors
- PMID: 37644471
- PMCID: PMC10466743
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-023-02123-x
Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern potentially expand host range to chickens: insights from AXL, NRP1 and ACE2 receptors
Abstract
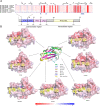
Background: The possibilities of cross-species transmission of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) between humans and poultry species are unknown. The analysis of the structure of receptor was used to investigate the potential of emerging SARS-CoV-2 VOCs to expand species tropism to chickens based on the interaction between Spike (S) protein and tyrosine kinase receptor UFO (AXL), angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and neuropilin 1 (NRP1) with substantial public health importance.
Methods: The structural and genetic alignment and surface potential analysis of the amino acid (aa) in ACE2, AXL, and NRP1 in human, hamster, mouse, mink, ferret, rhesus monkey and chickens were performed by Swiss-Model and pymol software. The critical aa sites that determined the susceptibility of the SARS-CoV-2 to the host were screened by aligning the residues interfacing with the N-terminal domain (NTD) or receptor-binding domain (RBD) of Spike protein.
Results: The binding modes of chickens AXL and ACE2 to S protein are similar to that of the ferret. The spatial structure and electrostatic surface potential of NRP1 showed that SARS-CoV-2 VOCs could not invade chickens through NRP1 easily.
Conclusion: These results suggested that emerging SARS-CoV-2 VOCs potentially expand the host range to chickens mainly through ACE2 and AXL receptors, while NRP1 receptor may rarely participate in the future epidemic of coronavirus disease 2019 in chickens.
Keywords: ACE2; AXL; Chickens; Cross-species transmission; NRP1; SARS-CoV-2 variants.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Susceptibility of bovine to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: insights from ACE2, AXL, and NRP1 receptors.Virol J. 2023 Nov 27;20(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02222-9. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 38012648 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical investigation of interactions between SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and neuropilin-1.Protein Sci. 2023 Oct;32(10):e4773. doi: 10.1002/pro.4773. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37656811 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of Mink ACE2 Binding to SARS-CoV-2 and Its Mink-Derived Variants.J Virol. 2022 Sep 14;96(17):e0081422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00814-22. Epub 2022 Aug 24. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36000849 Free PMC article.
-
The basis of mink susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection.J Appl Genet. 2022 Sep;63(3):543-555. doi: 10.1007/s13353-022-00689-w. Epub 2022 Apr 9. J Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 35396646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD): a structural perspective.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Mar;50(3):2713-2721. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-08193-4. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36562937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Screening for SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronaviruses in Urban Pigeons (Columbiformes) from the North of Spain under a 'One Health' Perspective.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):1143. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061143. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930525 Free PMC article.
-
Anexelekto (AXL) no more: microRNA-155 (miR-155) controls the "Uncontrolled" in SARS-CoV-2.Hum Cell. 2024 May;37(3):582-592. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01041-6. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38472734 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

