GREM1 signaling in cancer: tumor promotor and suppressor?
- PMID: 37615860
- PMCID: PMC10713512
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-023-00777-4
GREM1 signaling in cancer: tumor promotor and suppressor?
Abstract
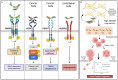
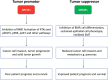
GREMLIN1 (GREM1) is member of a family of structurally and functionally related secreted cysteine knot proteins, which act to sequester and inhibit the action of multifunctional bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). GREM1 binds directly to BMP dimers, thereby preventing BMP-mediated activation of BMP type I and type II receptors. Multiple reports identify the overexpression of GREM1 as a contributing factor in a broad range of cancers. Additionally, the GREM1 gene is amplified in a rare autosomal dominant inherited form of colorectal cancer. The inhibitory effects of GREM1 on BMP signaling have been linked to these tumor-promoting effects, including facilitating cancer cell stemness and the activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Moreover, GREM1 has been described to bind and signal to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and stimulate angiogenesis, as well as epidermal and fibroblast growth factor receptor (EGFR and FGFR) to elicit tumor-promoting effects in breast and prostate cancer, respectively. In contrast, a 2022 report revealed that GREM1 can promote an epithelial state in pancreatic cancers, thereby inhibiting pancreatic tumor growth and metastasis. In this commentary, we will review these disparate findings and attempt to provide clarity around the role of GREM1 signaling in cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Zhichun Gao and Derek P. Brazil have no conflict interest. Peter ten Dijke and Julia Houthuijzen are supported by UCB for research on GREM1 in cancer progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
No evidence of Gremlin1-mediated activation of VEGFR2 signaling in endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 29;294(48):18041-18045. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC119.010148. Epub 2019 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31604823 Free PMC article.
-
Gremlin1 preferentially binds to bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and BMP-4 over BMP-7.Biochem J. 2015 Feb 15;466(1):55-68. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140771. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25378054
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived Gremlin 1 promotes breast cancer progression.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 18;21(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1194-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31533776 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and prospects of GREM1 research in cancer (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2023 Jul 19;19(3):69. doi: 10.3892/mco.2023.2665. eCollection 2023 Sep. Mol Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37614374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
Cited by
-
Hereditary Gastrointestinal Tumor Syndromes: When Risk Comes with Your Genes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 26;46(7):6440-6471. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070385. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification of Gremlin 1 throughout the tumor stroma using whole slide imaging and its clinicopathological significance in gastric cancer.Virchows Arch. 2024 Dec;485(6):1107-1116. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03903-8. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Virchows Arch. 2024. PMID: 39225725
References
-
- Biffi G, Spielman B, Hao Y. IL1-Induced JAK/STAT signaling is antagonized by TGFβ to shape CAF heterogeneity in pancreatic ductal. Adenocarcinoma ' Cancer Discovery. 2019;9(2):282–301. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

