Retrotransposons hijack alt-EJ for DNA replication and eccDNA biogenesis
- PMID: 37438532
- PMCID: PMC10691919
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06327-7
Retrotransposons hijack alt-EJ for DNA replication and eccDNA biogenesis
Abstract
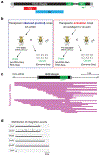
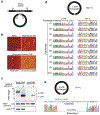
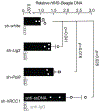
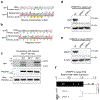
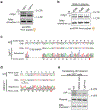
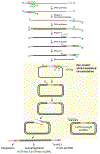
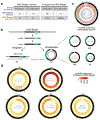
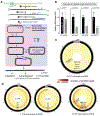
Retrotransposons are highly enriched in the animal genome1-3. The activation of retrotransposons can rewrite host DNA information and fundamentally impact host biology1-3. Although developmental activation of retrotransposons can offer benefits for the host, such as against virus infection, uncontrolled activation promotes disease or potentially drives ageing1-5. After activation, retrotransposons use their mRNA as templates to synthesize double-stranded DNA for making new insertions in the host genome1-3,6. Although the reverse transcriptase that they encode can synthesize the first-strand DNA1-3,6, how the second-strand DNA is generated remains largely unclear. Here we report that retrotransposons hijack the alternative end-joining (alt-EJ) DNA repair process of the host for a circularization step to synthesize their second-strand DNA. We used Nanopore sequencing to examine the fates of replicated retrotransposon DNA, and found that 10% of them achieve new insertions, whereas 90% exist as extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA). Using eccDNA production as a readout, further genetic screens identified factors from alt-EJ as essential for retrotransposon replication. alt-EJ drives the second-strand synthesis of the long terminal repeat retrotransposon DNA through a circularization process and is therefore necessary for eccDNA production and new insertions. Together, our study reveals that alt-EJ is essential in driving the propagation of parasitic genomic retroelements. Our study uncovers a conserved function of this understudied DNA repair process, and provides a new perspective to understand-and potentially control-the retrotransposon life cycle.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
Z.Z, F.Y., and W.S. are co-inventors on a US provisional patent application filed by Duke University related to this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
DNA-directed DNA polymerase and strand displacement activity of the reverse transcriptase encoded by the R2 retrotransposon.J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 23;374(2):322-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.047. Epub 2007 Sep 20. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17936300 Free PMC article.
-
The reverse transcriptase of the R2 non-LTR retrotransposon: continuous synthesis of cDNA on non-continuous RNA templates.J Mol Biol. 2002 Feb 22;316(3):459-73. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5369. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11866511
-
Sequencing the extrachromosomal circular mobilome reveals retrotransposon activity in plants.PLoS Genet. 2017 Feb 17;13(2):e1006630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006630. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28212378 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative end-joining repair pathways are the ultimate backup for abrogated classical non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination repair: Implications for the formation of chromosome translocations.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Nov;793:166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015. PMID: 26520387 Review.
-
"In the beginning": initiation of minus strand DNA synthesis in retroviruses and LTR-containing retrotransposons.Biochemistry. 2003 Dec 16;42(49):14349-55. doi: 10.1021/bi030201q. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14661945 Review.
Cited by
-
scCircle-seq unveils the diversity and complexity of extrachromosomal circular DNAs in single cells.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 27;15(1):1768. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45972-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38409079 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of extrachromosomal circular DNA in rice.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 18;15(1):2413. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46691-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38499575 Free PMC article.
-
Transposition of HOPPLA in siRNA-deficient plants suggests a limited effect of the environment on retrotransposon mobility in Brachypodium distachyon.PLoS Genet. 2024 Mar 12;20(3):e1011200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011200. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38470914 Free PMC article.
-
Insight on ecDNA-mediated tumorigenesis and drug resistance.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 11;10(6):e27733. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27733. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38545177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the Chromosome: Recent Developments in Decoding the Significance of Extrachromosomal Circular DNA (eccDNA) in Human Malignancies.Life (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;14(8):922. doi: 10.3390/life14080922. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

