Major β cell-specific functions of NKX2.2 are mediated via the NK2-specific domain
- PMID: 37364986
- PMCID: PMC10393193
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.350569.123
Major β cell-specific functions of NKX2.2 are mediated via the NK2-specific domain
Abstract
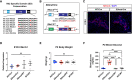
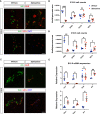
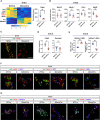
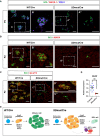
The consolidation of unambiguous cell fate commitment relies on the ability of transcription factors (TFs) to exert tissue-specific regulation of complex genetic networks. However, the mechanisms by which TFs establish such precise control over gene expression have remained elusive-especially in instances in which a single TF operates in two or more discrete cellular systems. In this study, we demonstrate that β cell-specific functions of NKX2.2 are driven by the highly conserved NK2-specific domain (SD). Mutation of the endogenous NKX2.2 SD prevents the developmental progression of β cell precursors into mature, insulin-expressing β cells, resulting in overt neonatal diabetes. Within the adult β cell, the SD stimulates β cell performance through the activation and repression of a subset of NKX2.2-regulated transcripts critical for β cell function. These irregularities in β cell gene expression may be mediated via SD-contingent interactions with components of chromatin remodelers and the nuclear pore complex. However, in stark contrast to these pancreatic phenotypes, the SD is entirely dispensable for the development of NKX2.2-dependent cell types within the CNS. Together, these results reveal a previously undetermined mechanism through which NKX2.2 directs disparate transcriptional programs in the pancreas versus neuroepithelium.
Keywords: NKX2.2; pancreatic islet; spinal cord; transcriptional regulation; β cells.
© 2023 Abarinov et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
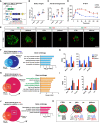
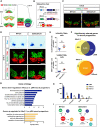
Similar articles
-
Differential use of the Nkx2.2 NK2 domain in developing pancreatic islets and neurons.Genes Dev. 2023 Jun 1;37(11-12):451-453. doi: 10.1101/gad.350895.123. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 37399332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nkx2.2 repressor complex regulates islet β-cell specification and prevents β-to-α-cell reprogramming.Genes Dev. 2011 Nov 1;25(21):2291-305. doi: 10.1101/gad.173039.111. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 22056672 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative transcriptional regulation of the essential pancreatic islet gene NeuroD1 (beta2) by Nkx2.2 and neurogenin 3.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 6;284(45):31236-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.048694. Epub 2009 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19759004 Free PMC article.
-
Mice lacking the homeodomain transcription factor Nkx2.2 have diabetes due to arrested differentiation of pancreatic beta cells.Development. 1998 Jun;125(12):2213-21. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.12.2213. Development. 1998. PMID: 9584121
-
Development and Characteristics of Pancreatic Epsilon Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 16;20(8):1867. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081867. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31014006 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential use of the Nkx2.2 NK2 domain in developing pancreatic islets and neurons.Genes Dev. 2023 Jun 1;37(11-12):451-453. doi: 10.1101/gad.350895.123. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 37399332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmentally dynamic changes in DNA methylation in the human pancreas.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jun 3;25(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10450-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38831310 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
