RNF43 is a novel tumor-suppressor and prognostic indicator in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 37304674
- PMCID: PMC10208019
- DOI: 10.32604/or.2022.03458
RNF43 is a novel tumor-suppressor and prognostic indicator in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
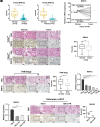
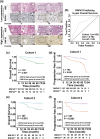
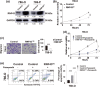
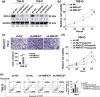
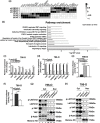
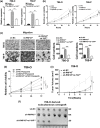
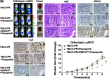
Identifying prognostic indicators of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and elucidating the mechanisms underlying ccRCC progression are crucial for improving ccRCC patient prognosis. This study investigated the clinical significance and biological role of Ring finger protein 43 (RNF43) in ccRCC. Two independent cohorts of patients with ccRCC were employed to determine the prognostic significance of RNF43 by immunohistochemistry and statistical analyses. In vitro and in vivo experiments, RNA-seq, and other techniques were used to determine the biological role of RNF43 in ccRCC and related molecular mechanisms. RNF43 expression was commonly decreased in ccRCC specimens, and low expression of RNF43 indicated a higher TNM stage, SSIGN score, and WHO/ISUP grade and short survival in patients with ccRCC. Additionally, RNF43 overexpression suppressed the proliferation, migration, and targeted drug resistance of ccRCC cells, while the knockdown of RNF43 enhanced these characteristics of ccRCC. RNF43 knockdown activated YAP signaling by decreasing YAP phosphorylation by p-LATS1/2 and increasing the transcription and nuclear distribution of YAP. By contrast, RNF43 overexpression showed the opposite effects. Decreasing YAP abolished the effect of RNF43 knockdown in promoting the malignant features of ccRCC. Additionally, restoring RNF43 expression suppressed the resistance of the targeted drug pazopanib in in vivo orthotopic ccRCC. Furthermore, combining the expression of RNF43 and YAP with TNM stage or the SSIGN score exhibited greater accuracy than any of these indicators alone in assessing the postoperative prognosis of ccRCC patients. In summary, our study identified a novel tumor suppressor, RNF43, which is also a prognostic indicator and potential target for ccRCC.
Keywords: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; RNF43, Prognosis; YAP, Tumor progression.
© 2021 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNF43 is a Novel Tumor Suppressor and Prognostic Indicator in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Oncol Res. 2021 Jul 2. doi: 10.3727/096504021X16252201000833. Online ahead of print. Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34215350
-
Integrating HECW1 expression into the clinical indicators exhibits high accuracy in assessing the prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Aug 4;21(1):890. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08631-9. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34348693 Free PMC article.
-
Combining expression of RNF43 and infiltration level of CD163+ tumor associated macrophage predicts prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(4):3962-3971. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5229. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36097369 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting a positive regulatory loop in the tumor-macrophage interaction impairs the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Mar;28(3):932-951. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00626-6. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 33009518 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Management of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Novel Biomarkers and Targeted Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 16;15(12):3207. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123207. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hereditary Gastrointestinal Tumor Syndromes: When Risk Comes with Your Genes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 26;46(7):6440-6471. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070385. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deubiquitinase USP14 is upregulated in Crohn's disease and inhibits the NOD2 pathway mediated inflammatory response in vitro.Eur J Histochem. 2024 Sep 9;68(3):4101. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4101. Eur J Histochem. 2024. PMID: 39252535 Free PMC article.
-
RNF43 mutation as a predictor of immunotherapeutic efficacy in colorectal cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 15;13(11):5549-5558. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38058823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li, S., Lavrijsen, M., Bakker, A., Magierowski, M., Magierowska, K.et al. (2020). Commonly observed RNF43 mutations retain functionality in attenuating Wnt/β-catenin signaling and unlikely confer Wnt-dependency onto colorectal cancers. Oncogene , 39(17), 3458–3472. DOI 10.1038/s41388-020-1232-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
