A Genetic Locus within the FMN1/GREM1 Gene Region Interacts with Body Mass Index in Colorectal Cancer Risk
- PMID: 37249599
- PMCID: PMC10391330
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3713
A Genetic Locus within the FMN1/GREM1 Gene Region Interacts with Body Mass Index in Colorectal Cancer Risk
Abstract
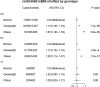
Colorectal cancer risk can be impacted by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, including diet and obesity. Gene-environment interactions (G × E) can provide biological insights into the effects of obesity on colorectal cancer risk. Here, we assessed potential genome-wide G × E interactions between body mass index (BMI) and common SNPs for colorectal cancer risk using data from 36,415 colorectal cancer cases and 48,451 controls from three international colorectal cancer consortia (CCFR, CORECT, and GECCO). The G × E tests included the conventional logistic regression using multiplicative terms (one degree of freedom, 1DF test), the two-step EDGE method, and the joint 3DF test, each of which is powerful for detecting G × E interactions under specific conditions. BMI was associated with higher colorectal cancer risk. The two-step approach revealed a statistically significant G×BMI interaction located within the Formin 1/Gremlin 1 (FMN1/GREM1) gene region (rs58349661). This SNP was also identified by the 3DF test, with a suggestive statistical significance in the 1DF test. Among participants with the CC genotype of rs58349661, overweight and obesity categories were associated with higher colorectal cancer risk, whereas null associations were observed across BMI categories in those with the TT genotype. Using data from three large international consortia, this study discovered a locus in the FMN1/GREM1 gene region that interacts with BMI on the association with colorectal cancer risk. Further studies should examine the potential mechanisms through which this locus modifies the etiologic link between obesity and colorectal cancer.
Significance: This gene-environment interaction analysis revealed a genetic locus in FMN1/GREM1 that interacts with body mass index in colorectal cancer risk, suggesting potential implications for precision prevention strategies.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of Body Mass Index With Colorectal Cancer Risk by Genome-Wide Variants.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021 Jan 4;113(1):38-47. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djaa058. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021. PMID: 32324875 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of genetic risk variants for other cancers on colorectal cancer risk: PAGE, GECCO and CCFR consortia.Gut. 2014 May;63(5):800-7. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305189. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Gut. 2014. PMID: 23935004 Free PMC article.
-
SNPs associated with colorectal cancer at 15q13.3 affect risk enhancers that modulate GREM1 gene expression.Hum Mutat. 2021 Mar;42(3):237-245. doi: 10.1002/humu.24166. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Hum Mutat. 2021. PMID: 33476087 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-environment interaction involving recently identified colorectal cancer susceptibility Loci.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 Sep;23(9):1824-33. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0062. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014. PMID: 24994789 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Genetic Susceptibility Loci for Colorectal Tumors in a Genome-Wide Meta-analysis.Gastroenterology. 2013 Apr;144(4):799-807.e24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.12.020. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23266556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hereditary Gastrointestinal Tumor Syndromes: When Risk Comes with Your Genes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 26;46(7):6440-6471. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070385. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiposity and cancer: meta-analysis, mechanisms, and future perspectives.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 18:2024.02.16.24302944. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.16.24302944. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38405761 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Murphy N, Moreno V, Hughes DJ, Vodicka L, Vodicka P, Aglago EK, et al. . Lifestyle and dietary environmental factors in colorectal cancer susceptibility. Mol Aspects Med 2019;69:2–9. - PubMed
-
- Islami F, Goding Sauer A, Miller KD, Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Jacobs EJ, et al. . Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:31–54. - PubMed
-
- Campbell PT. Obesity: a certain and avoidable cause of cancer. Lancet 2014;384:727–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA154337/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA167551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042182/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA196569/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- R01 CA059045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA197350/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076366/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197735/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA114347/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA072520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028685/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA151993/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA048998/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA137088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010200/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA066635/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA206110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA201407/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA033619/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA086308/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA153323/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201700006I/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES013678/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA254108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 14136/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA152715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA122839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA084968/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010200/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M012190/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA097325/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG018033/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States

