G-Quadruplexes in Nuclear Biomolecular Condensates
- PMID: 37239436
- PMCID: PMC10218287
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14051076
G-Quadruplexes in Nuclear Biomolecular Condensates
Abstract
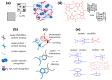
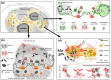
G-quadruplexes (G4s) have long been implicated in the regulation of chromatin packaging and gene expression. These processes require or are accelerated by the separation of related proteins into liquid condensates on DNA/RNA matrices. While cytoplasmic G4s are acknowledged scaffolds of potentially pathogenic condensates, the possible contribution of G4s to phase transitions in the nucleus has only recently come to light. In this review, we summarize the growing evidence for the G4-dependent assembly of biomolecular condensates at telomeres and transcription initiation sites, as well as nucleoli, speckles, and paraspeckles. The limitations of the underlying assays and the remaining open questions are outlined. We also discuss the molecular basis for the apparent permissive role of G4s in the in vitro condensate assembly based on the interactome data. To highlight the prospects and risks of G4-targeting therapies with respect to the phase transitions, we also touch upon the reported effects of G4-stabilizing small molecules on nuclear biomolecular condensates.
Keywords: G-quadruplex; chromatin structure; liquid–liquid phase separation; membraneless condensates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
G-Quadruplex Structures Colocalize with Transcription Factories and Nuclear Speckles Surrounded by Acetylated and Dimethylated Histones H3.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 17;22(4):1995. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041995. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671470 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel light-up probe for detection of G-quadruplexes in stress granules.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 28;12(1):12892. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17230-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35902691 Free PMC article.
-
G-Quadruplex-Induced Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Biomimetic Protocells.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Jul 28;143(29):11036-11043. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c03627. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 34270902
-
Structurally diverse G-quadruplexes as the noncanonical nucleic acid drug target for live cell imaging and antibacterial study.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Feb 2;59(11):1415-1433. doi: 10.1039/d2cc05945b. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 36636928 Review.
-
Nuclear Protein Condensates and Their Properties in Regulation of Gene Expression.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 15;434(1):167151. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167151. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34271007 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein G-quadruplex interactions and their effects on phase transitions and protein aggregation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 8;52(8):4702-4722. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae229. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38572746 Free PMC article.
-
The strand exchange domain of tumor suppressor PALB2 is intrinsically disordered and promotes oligomerization-dependent DNA compaction.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 29:2023.06.01.543259. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.01.543259. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: iScience. 2024 Oct 28;27(12):111259. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111259. PMID: 37333393 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Roles of Nucleic Acids in Protein Folding, Aggregation, and Disease.ACS Chem Biol. 2024 Apr 19;19(4):809-823. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00695. Epub 2024 Mar 13. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38477936 Review.
-
Protein G-quadruplex interactions and their effects on phase transitions and protein aggregation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 20:2023.09.21.558871. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.21.558871. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 8;52(8):4702-4722. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae229. PMID: 37790366 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

