Phase II Investigation of TVB-2640 (Denifanstat) with Bevacizumab in Patients with First Relapse High-Grade Astrocytoma
- PMID: 37093199
- PMCID: PMC10320469
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2807
Phase II Investigation of TVB-2640 (Denifanstat) with Bevacizumab in Patients with First Relapse High-Grade Astrocytoma
Abstract
Purpose: Glioblastoma represents the most common primary brain tumor. Although antiangiogenics are used in the recurrent setting, they do not prolong survival. Glioblastoma is known to upregulate fatty acid synthase (FASN) to facilitate lipid biosynthesis. TVB-2640, a FASN inhibitor, impairs this activity.
Patients and methods: We conducted a prospective, single-center, open-label, unblinded, phase II study of TVB-2640 plus bevacizumab in patients with recurrent high-grade astrocytoma. Patients were randomly assigned to TVB-2640 (100 mg/m2 oral daily) plus bevacizumab (10 mg/kg i.v., D1 and D15) or bevacizumab monotherapy for cycle 1 only (28 days) for biomarker analysis. Thereafter, all patients received TVB-2640 plus bevacizumab until treatment-related toxicity or progressive disease (PD). The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS).
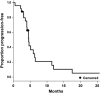
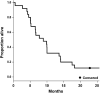
Results: A total of 25 patients were enrolled. The most frequently reported adverse events (AE) were palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, hypertension, mucositis, dry eye, fatigue, and skin infection. Most were grade 1 or 2 in intensity. The overall response rate (ORR) for TVB-2640 plus bevacizumab was 56% (complete response, 17%; partial response, 39%). PFS6 for TVB-2640 plus bevacizumab was 31.4%. This represented a statistically significant improvement in PFS6 over historical bevacizumab monotherapy (BELOB 16%; P = 0.008) and met the primary study endpoint. The observed OS6 was 68%, with survival not reaching significance by log-rank test (P = 0.56).
Conclusions: In this phase II study of relapsed high-grade astrocytoma, TVB-2640 was found to be a well-tolerated oral drug that could be safely combined with bevacizumab. The favorable safety profile and response signals support the initiation of a larger multicenter trial of TVB-2640 plus bevacizumab in astrocytoma.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-agent bevacizumab or lomustine versus a combination of bevacizumab plus lomustine in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (BELOB trial): a randomised controlled phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Aug;15(9):943-53. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70314-6. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25035291 Clinical Trial.
-
Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone as second-line treatment for patients with HER2-negative locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer after first-line treatment with bevacizumab plus chemotherapy (TANIA): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Oct;15(11):1269-78. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70439-5. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25273342 Clinical Trial.
-
Bevacizumab and paclitaxel-carboplatin chemotherapy and secondary cytoreduction in recurrent, platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer (NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group study GOG-0213): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Jun;18(6):779-791. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30279-6. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28438473 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase 1 and randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial of bevacizumab plus dasatinib in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: Alliance/North Central Cancer Treatment Group N0872.Cancer. 2019 Nov 1;125(21):3790-3800. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32340. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31290996 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENT-32): a randomised, open-label, phase 2-3 study.Lancet Oncol. 2021 Jul;22(7):977-990. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00252-7. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Lancet Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34143971 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The SARIFA biomarker in the context of basic research of lipid-driven cancers.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 Jul 31;8(1):165. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00662-2. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39085485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of endothelial cells in brain tumours.Clin Transl Med. 2023 Oct;13(10):e1433. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1433. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37830128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Insights and Radiation-Immuno-Oncology Developments in Primary and Secondary Brain Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 28;16(11):2047. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112047. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Metabolic Reprogramming in Tumor Evolution and Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;16(20):3513. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203513. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Principles in the Management of Glioblastoma.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 17;15(4):501. doi: 10.3390/genes15040501. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Gilbert MR, Chakravarti A. Chemoradiotherapy in malignant glioma: standard of care and future directions. J Clin Oncol 2007;25:4127–36. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJB, et al. . Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005;352:987–96. - PubMed
-
- Liau LM, Ashkan K, Brem S, Campian JL, Trusheim JE, Iwamoto FM, et al. . Association of autologous tumor lysate-loaded dendritic cell vaccination with extension of survival among patients with newly diagnosed and recurrent glioblastoma: a phase 3 prospective externally controlled cohort trial. JAMA Oncol 2023;9:112–21. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, et al. . Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:4733–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous