The role of short-chain fatty acids in inflammatory skin diseases
- PMID: 36817115
- PMCID: PMC9932284
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1083432
The role of short-chain fatty acids in inflammatory skin diseases
Abstract
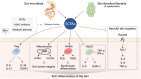
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are metabolites of gut microbes that can modulate the host inflammatory response, and contribute to health and homeostasis. Since the introduction of the gut-skin axis concept, the link between SCFAs and inflammatory skin diseases has attracted considerable attention. In this review, we have summarized the literature on the role of SCFAs in skin inflammation, and the correlation between SCFAs and inflammatory skin diseases, especially atopic dermatitis, urticaria, and psoriasis. Studies show that SCFAs are signaling factors in the gut-skin axis and can alleviate skin inflammation. The information presented in this review provides new insights into the molecular mechanisms driving gut-skin axis regulation, along with possible pathways that can be targeted for the treatment and prevention of inflammatory skin diseases.
Keywords: acne; atopic dermatitis; eczema; histone deacetylase (HDAC); inflammatory skin disease; psoriasis; short-chain fatty acid (SCFA); urticaria.
Copyright © 2023 Xiao, Hu, Yao, Cao, Zou, Wang, Qin, Zhong, Li, Xue, Jin, Li, Shi and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilar E. C., Silva J. F. D., Navia-Pelaez J. M., Leonel A. J., Lopes L. G., Menezes-Garcia Z., et al. (2018). Sodium butyrate modulates adipocyte expansion, adipogenesis, and insulin receptor signaling by upregulation of PPAR-γ in obese apo E knockout mice. Nutrition 47 75–82. 10.1016/j.nut.2017.10.007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

