Transcriptome-based analysis of key pathways relating to yield formation stage of foxtail millet under different drought stress conditions
- PMID: 36816479
- PMCID: PMC9937063
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1110910
Transcriptome-based analysis of key pathways relating to yield formation stage of foxtail millet under different drought stress conditions
Abstract
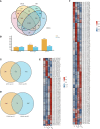
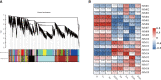
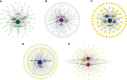
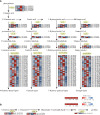
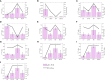
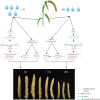
Although foxtail millet, as small Panicoid crop, is of drought resilient, drought stress has a significant effect on panicle of foxtail millet at the yield formation stage. In this study, the changes of panicle morphology, photosynthesis, antioxidant protective enzyme system, reactive oxygen species (ROS) system, and osmotic regulatory substance and RNA-seq of functional leaves under light drought stress (LD), heavy drought stress (HD), light drought control (LDCK) and heavy drought control (HDCK) were studied to get a snap-shot of specific panicle morphological changes, physiological responses and related molecular mechanisms. The results showed that the length and weight of panicle had decreased, but with increased empty abortive rate, and then yield dropped off 14.9% and 36.9%, respectively. The photosynthesis of millet was significantly decreased, like net photosynthesis rate, stomatal conductance and transpiration rate, especially under HD treatment with reluctant recovery from rehydration. Under LD and HD treatment, the peroxidase (POD) was increased by 34% and 14% and the same as H2O2 by 34.7% and 17.2% compared with LDCK and HDCK. The ability to produce and inhibit O2- free radicals under LD treatment was higher than HD. The content of soluble sugar was higher under LD treatment but the proline was higher under HD treatment. Through RNA-seq analysis, there were 2,393 and 3,078 different genes expressed under LD and HD treatment. According to the correlation analysis between weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA) and physiological traits, the co-expression network of several modules with high correlation was constructed, and some hub genes of millet in response to drought stress were found. The expression changes relating to carbon fixation, sucrose and starch synthesis, lignin synthesis, gibberellin synthesis, and proline synthesis of millet were specifically analyzed. These findings provide a full perspective on how drought affects the yield formation of foxtail millet by constructing one work model thereby providing theoretical foundation for hub genes exploration and drought resistance breeding of foxtail millet.
Keywords: DEGs; RNA-seq; drought stress; foxtail millet; physiological index; yield formation.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Sun, Wang, Tang, Li, Ren, Ren, Wang, Jiang, Zhong, Zhao, Zhang, Liu, Kang, Zhao and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Gene Expression Profiles Analysis Reveal Novel Insights into Drought Stress in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 12;21(22):8520. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228520. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33198267 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals a coexpression network of the carotenoid metabolism pathway in the panicle of Setaria italica.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Mar 8;22(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03467-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35260077 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on cell structure and stress resistance physiology of Setaria italica under drought stress.Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2023 May;34(5):1281-1289. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202305.015. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37236945 English.
-
Foxtail millet: a model crop for genetic and genomic studies in bioenergy grasses.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2013 Sep;33(3):328-43. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2012.716809. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22985089 Review.
-
Adaptation of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.) to Abiotic Stresses: A Special Perspective of Responses to Nitrogen and Phosphate Limitations.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 28;11:187. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00187. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32184798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Foxtail Millet bZIP Transcription Factor SibZIP67 Enhances Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 7;14(8):958. doi: 10.3390/biom14080958. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199345 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic alterations in Castor (Ricinus communis L.) under polyethylene glycol-induced oxidative stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Oct 17;24(1):973. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05691-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39415088 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and expression analysis of bZIP transcription factors in Setaria italica in response to dehydration stress.Front Genet. 2024 Aug 30;15:1466486. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1466486. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39280094 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of shading on morphology, photosynthesis characteristics, and yield of different shade-tolerant peanut varieties at the flowering stage.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 8;15:1429800. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1429800. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai Y., Feng Z., Paerhati M., Wang J. (2021). Phenylpropanoid metabolism enzyme activities and gene expression in postharvest melons inoculated with Alternaria alternate . Appl. Biol. Chem. 64, 83. doi: 10.1186/s13765-021-00654-x - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

