Targeting epigenetic regulators to overcome drug resistance in cancers
- PMID: 36797239
- PMCID: PMC9935618
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01341-7
Targeting epigenetic regulators to overcome drug resistance in cancers
Abstract
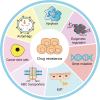
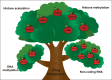
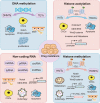
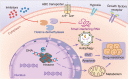
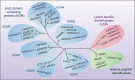
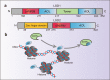
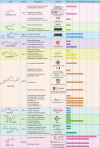
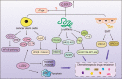
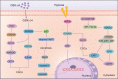
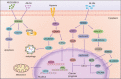
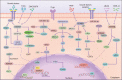
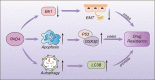
Drug resistance is mainly responsible for cancer recurrence and poor prognosis. Epigenetic regulation is a heritable change in gene expressions independent of nucleotide sequence changes. As the common epigenetic regulation mechanisms, DNA methylation, histone modification, and non-coding RNA regulation have been well studied. Increasing evidence has shown that aberrant epigenetic regulations contribute to tumor resistance. Therefore, targeting epigenetic regulators represents an effective strategy to reverse drug resistance. In this review, we mainly summarize the roles of epigenetic regulation in tumor resistance. In addition, as the essential factors for epigenetic modifications, histone demethylases mediate the histone or genomic DNA modifications. Herein, we comprehensively describe the functions of the histone demethylase family including the lysine-specific demethylase family, the Jumonji C-domain-containing demethylase family, and the histone arginine demethylase family, and fully discuss their regulatory mechanisms related to cancer drug resistance. In addition, therapeutic strategies, including small-molecule inhibitors and small interfering RNA targeting histone demethylases to overcome drug resistance, are also described.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic gene regulation by plant Jumonji group of histone demethylase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1809(8):421-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21419882 Review.
-
Development of JmjC-domain-containing histone demethylase (KDM2-7) inhibitors for cancer therapy.Drug Discov Today. 2023 May;28(5):103519. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103519. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 36754142 Review.
-
Histone demethylases in physiology and cancer: a tale of two enzymes, JMJD3 and UTX.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Feb;36:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 May 3. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27151432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of histone H3 lysine demethylases in glioblastoma.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Jun;42(2):445-454. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10114-1. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37286866 Review.
-
The role of the histone demethylase KDM4A in cancer.Cancer Genet. 2015 May;208(5):215-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Cancer Genet. 2015. PMID: 25633974 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Role of HGF/c-Met Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9101. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169101. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering prostate cancer in vitro: what does it take?Oncogene. 2023 Aug;42(32):2417-2427. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02776-6. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 37438470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the study of posttranslational modifications of histones in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Nov 21;16(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01785-w. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39574168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organoids: An Emerging Precision Medicine Model for Prostate Cancer Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 16;25(2):1093. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021093. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sintilimab combined with anlotinib and chemotherapy as second-line or later therapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: a phase II clinical trial.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 16;9(1):241. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01957-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39278918 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

