Nutritional Quality of Plant-Based Meat and Dairy Imitation Products and Comparison with Animal-Based Counterparts
- PMID: 36678272
- PMCID: PMC9862700
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15020401
Nutritional Quality of Plant-Based Meat and Dairy Imitation Products and Comparison with Animal-Based Counterparts
Abstract
While consumers are increasingly adopting plant-based meat and dairy imitation products, the nutritional quality and adequacy of those foods to act as a substitute is still under discussion. The Greek Branded Food Composition Database (HelTH) was expanded to map currently available meat and dairy imitations in Greece. Their main ingredient used, nutritional composition, and promotion as a healthy, nutritious food were described, and their overall nutritional quality using the Nutri-Score algorithm was evaluated. A total of n = 421 plant-based imitations were analyzed, made primarily of wheat or wheat mixes (83.5%) for meat imitations and grain (19.8%) or vegetable oil (17.1%) for dairy imitations. All meat imitations were high in protein and fiber, while, for dairy, only yogurts carried a protein content claim (80.9%). Imitation sausages, milk, and yogurt products had lower total fat and saturated fat content compared to their animal-based counterparts. All dairy imitations had lower protein content than animal-based dairy. The nutritional quality of imitation cheeses was graded as D-E, under the Nutri-Score system, compared to A-C for the animal-based cheese. Plant-based imitations have variable composition based on their main ingredient, and the substitution of specific food groups with plant-based alternatives may not support an equivalent or improved diet.
Keywords: Nutri-Score; alternative protein sources; branded food composition database; dairy imitations; dairy substitutes; meat imitations; meat substitutes; nutritional composition; plant-based diet; vegan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
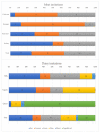
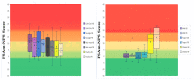
Similar articles
-
Nutri-Score of Meat, Fish, and Dairy Alternatives: A Comparison between the Old and New Algorithm.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 19;16(6):892. doi: 10.3390/nu16060892. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542803 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional quality and price of plant-based dairy and meat analogs in the Canadian food supply system.J Food Sci. 2023 Aug;88(8):3594-3606. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16691. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37458282
-
Are plant-based alternatives healthier? A two-dimensional evaluation from nutritional and processing standpoints.Food Res Int. 2023 Jul;169:112857. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112857. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Food Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37254431
-
Nutritional Profile of Commercialized Plant-Based Meat: An Integrative Review with a Systematic Approach.Foods. 2023 Jan 18;12(3):448. doi: 10.3390/foods12030448. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36765980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel animal product substitutes: A new category of plant-based alternatives to meat, seafood, egg, and dairy products.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2024 May;23(3):e313330. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.13330. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2024. PMID: 38551190 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional analysis of vegan recipes: From social media to plate.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Aug 2;12(10):7657-7670. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4382. eCollection 2024 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39479681 Free PMC article.
-
Health and functional advantages of cheese containing soy protein and soybean-derived casein.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jul 23;15:1407506. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1407506. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39109061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision Food Composition Data as a Tool to Decipher the Riddle of Ultra-Processed Foods and Nutritional Quality.Foods. 2024 Apr 19;13(8):1259. doi: 10.3390/foods13081259. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38672931 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Physical and Compositional Attributes between Commercial Plant-Based and Dairy Yogurts.Foods. 2024 Mar 23;13(7):984. doi: 10.3390/foods13070984. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38611291 Free PMC article.
-
Nutri-Score of Meat, Fish, and Dairy Alternatives: A Comparison between the Old and New Algorithm.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 19;16(6):892. doi: 10.3390/nu16060892. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gustafson D.I., Decker E.A., Drewnowski A., Hamm M.W., Hwang J., Merrigan K.A. Making Healthy, Sustainable Diets Accessible and Achievable: A New Framework for Assessing the Nutrition, Environmental, and Equity Impacts of Packaged Foods. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2022;6:nzac136. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzac136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gastaldello A., Giampieri F., De Giuseppe R., Grosso G., Baroni L., Battino M. The rise of processed meat alternatives: A narrative review of the manufacturing, composition, nutritional profile and health effects of newer sources of protein, and their place in healthier diets. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022;127:263–271. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.07.005. - DOI
-
- Romão B., Botelho R.B.A., Nakano E.Y., Raposo A., Han H., Vega-Muñoz A., Ariza-Montes A., Zandonadi R.P. Are Vegan Alternatives to Meat Products Healthy? A Study on Nutrients and Main Ingredients of Products Commercialized in Brazil. Front. Public Health. 2022;10:1565. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.900598. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magkos F., Tetens I., Bügel S.G., Felby C., Schacht S.R., Hill J.O., Ravussin E., Astrup A. A Perspective on the Transition to Plant-Based Diets: A Diet Change May Attenuate Climate Change, but Can It Also Attenuate Obesity and Chronic Disease Risk? Advances in Nutrition. 2020;11:1. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz090. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Plant-Based Diets and Their Impact on Health, Sustainability and the Environment A Review of the Evidence WHO European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. 2021. [(accessed on 23 December 2022)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/349086.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

