JAK inhibitors disrupt T cell-induced proinflammatory macrophage activation
- PMID: 36599629
- PMCID: PMC9815080
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002671
JAK inhibitors disrupt T cell-induced proinflammatory macrophage activation
Abstract
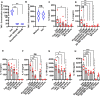
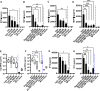
Objectives: Macrophage subsets, activated by T cells, are increasingly recognised to play a central role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors have proven beneficial clinical effects in RA. In this study, we investigated the effect of JAK inhibitors on the generation of cytokine-activated T (Tck) cells and the production of cytokines and chemokines induced by Tck cell/macrophage interactions.
Methods: CD14+ monocytes and CD4+ T cells were purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells from buffy coats of healthy donors. As representative JAK inhibitors, tofacitinib or ruxolitinib were added during Tck cell differentiation. Previously validated protocols were used to generate macrophages and Tck cells from monocytes and CD4+ T cells, respectively. Cytokine and chemokine including TNF, IL-6, IL-15, IL-RA, IL-10, MIP1α, MIP1β and IP10 were measured by ELISA.
Results: JAK inhibitors prevented cytokine-induced maturation of Tck cells and decreased the production of proinflammatory cytokines TNF, IL-6, IL-15, IL-1RA and the chemokines IL-10, MIP1α, MIP1β, IP10 by Tck cell-activated macrophages in vitro (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Our findings show that JAK inhibition disrupts T cell-induced macrophage activation and reduces downstream proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine responses, suggesting that suppressing the T cell-macrophage interaction contributes to the therapeutic effect of JAK inhibitors.
Keywords: T-lymphocyte subsets; antirheumatic agents; arthritis, rheumatoid; chemokines; inflammation.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DP has received consultancy and sponsorship from Abbvie and Eli Lilly to attend scientific meetings. SS has received institutional research grants from Amgen (previously Celgene), Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Janssen, and UCB; and honoraria/speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, and UCB. IBM has received consultancy and research support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Abbvie, Eli Lilly and Gilead, all of whom manufacture inhibitors of JAKs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokine-stimulated T cells induce macrophage IL-10 production dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p70S6K: implications for rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res. 2002;4(1):64-70. doi: 10.1186/ar385. Epub 2001 Oct 10. Arthritis Res. 2002. PMID: 11879539 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of inflammatory responses in tumor necrosis factor-activated and rheumatoid arthritis synovial macrophages by JAK inhibitors.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Dec;64(12):3856-66. doi: 10.1002/art.37691. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22941906 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Activated Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Peficitinib.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 26;10:541. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00541. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30984167 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into IFN-γ in rheumatoid arthritis: role in the era of JAK inhibitors.Immunol Med. 2020 Jun;43(2):72-78. doi: 10.1080/25785826.2020.1751908. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Immunol Med. 2020. PMID: 32338187 Review.
-
Monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Circulating precursors of macrophages and osteoclasts and, their heterogeneity and plasticity role in RA pathogenesis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Dec;65:348-359. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.10.016. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30366278 Review.
Cited by
-
JAK Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Immunomodulatory Properties and Clinical Efficacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 30;25(15):8327. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158327. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations of the circulating levels of cytokines with the risk of myeloproliferative neoplasms: a bidirectional mendelian-randomization study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 26;24(1):531. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12301-x. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38671390 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage re-programming by JAK inhibitors relies on MAFB.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Mar 25;81(1):152. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05196-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38528207 Free PMC article.
-
Validated graft-specific biomarkers identify patients at risk for chronic graft-versus-host disease and death.J Clin Invest. 2023 Aug 1;133(15):e168575. doi: 10.1172/JCI168575. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37526081 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment: Clinical and Natural Product Interventions Explored.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 2;24(13):11004. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311004. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
