Current understanding of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway: Structure, regulatory mechanisms, and related diseases
- PMID: 36579404
- PMCID: PMC9841179
- DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.464
Current understanding of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway: Structure, regulatory mechanisms, and related diseases
Abstract
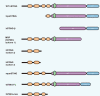
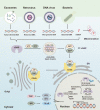
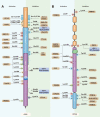
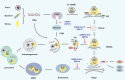
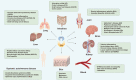
The innate immune system protects the host from external pathogens and internal damage in various ways. The cGAS-STING signaling pathway, comprised of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), stimulator of interferon genes (STING), and downstream signaling adaptors, plays an essential role in protective immune defense against microbial DNA and internal damaged-associated DNA and is responsible for various immune-related diseases. After binding with DNA, cytosolic cGAS undergoes conformational change and DNA-linked liquid-liquid phase separation to produce 2'3'-cGAMP for the activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-localized STING. However, further studies revealed that cGAS is predominantly expressed in the nucleus and strictly tethered to chromatin to prevent binding with nuclear DNA, and functions differently from cytosolic-localized cGAS. Detailed delineation of this pathway, including its structure, signaling, and regulatory mechanisms, is of great significance to fully understand the diversity of cGAS-STING activation and signaling and will be of benefit for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. Here, we review recent progress on the above-mentioned perspectives of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway and discuss new avenues for further study.
先天免疫系统是宿主免疫防御的第一道防线,其通过多种机制保护宿主抵御外源病原入侵及内源损伤。cGAS-STING信号通路是先天免疫的重要通路之一,其由环磷酸鸟苷-磷酸腺苷酸合成酶(cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, cGAS)、干扰素基因刺激物(stimulator of interferon gene,STING)和一系列下游信号转导接头分子及效应分子共同组成。cGAS是一种DNA感受器,在与DNA结合后,细胞质中的cGAS发生构象变化并由DNA介导聚集形成液-液相分离。随后,cGAS催化ATP和GTP合成第二信使2'3'-cGAMP,以激活定位于内质网(endoplasmic reticulum, ER)的STING,诱导STING转运并介导下游I型干扰素的产生。近年来研究发现,除了定位于细胞质发挥DNA识别受体的功能外,cGAS更主要在细胞核中表达,并被束缚于染色质以防止其与核DNA的结合,避免自身免疫疾病的发生。在功能上,核定位的cGAS与细胞质cGAS也具有较大差异。此外,cGAS-STING信号通路的异常也与多种疾病的发生密切相关。因此,对于cGAS-STING的结构,信号转导和调控机制方面的系统性探究,将更有助于我们深入了解该信号通路的活化和信号传递机制,并将为免疫相关疾病和肿瘤的治疗提供新的方向。基于此,该文详细综述了cGAS-STING信号通路目前的研究进展,并对其将来的研究方向提出展望。.
Keywords: Diseases; Post-translational modification; STING; Signaling; Structure; cGAS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The cGAS-STING Pathway: Novel Perspectives in Liver Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 29;12:682736. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.682736. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between the SFTSV envelope glycoprotein Gn and STING inhibits the formation of the STING-TBK1 complex and suppresses the NF-κB signaling pathway.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0181523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01815-23. Epub 2024 Feb 29. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38421179 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress on the activation of the cGAS-STING pathway and its regulation by biomolecular condensation.J Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Nov 29;14(6):mjac042. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac042. J Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35803579 Free PMC article.
-
Potential cGAS-STING pathway functions in DNA damage responses, DNA replication and DNA repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Jan;133:103608. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2023.103608. Epub 2023 Nov 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38056369 Review.
-
The cGAS-STING Pathway in Bacterial Infection and Bacterial Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:814709. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.814709. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
cGAS-STING signaling pathway in intestinal homeostasis and diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 14;14:1239142. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1239142. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37781354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of letters to the editor and publications in 2023.Zool Res. 2024 Jan 18;45(1):136-137. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2023.378. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 38114439 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
cGAS/STING in skin melanoma: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Nov 18;22(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01860-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39558334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosomal Instability-Driven Cancer Progression: Interplay with the Tumour Microenvironment and Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2023 Nov 26;12(23):2712. doi: 10.3390/cells12232712. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Pulmonary Fibrosis-like Changes in the Setting of Heat Exposure: DNA Damage and Cell Senescence.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 5;25(5):2992. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052992. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474239 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
