Mechanism and Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Osteosarcoma
- PMID: 36551309
- PMCID: PMC9775044
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12121882
Mechanism and Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Osteosarcoma
Abstract
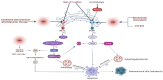
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant bone tumor, often occurring in children and adolescents. The etiology of most patients is unclear, and the current conventional treatment methods are chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical resection. However, the sensitivity of osteosarcoma to radiotherapy and chemotherapy is low, and the prognosis is poor. The development of new and useful treatment strategies for improving patient survival is an urgent need. It has been found that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress (ERS) affects tumor angiogenesis, invasion, etc. By summarizing the literature related to osteosarcoma and ERS, we found that the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway activated by ERS has a regulatory role in osteosarcoma proliferation, apoptosis, and chemoresistance. In osteosarcoma, the UPR pathway plays an important role by crosstalk with autophagy, oxidative stress, and other pathways. Overall, this article focuses on the relationship between ERS and osteosarcoma and reviews the potential of drugs or gene targets associated with ERS for the treatment of osteosarcoma.
Keywords: autophagy; endoplasmic reticulum stress; osteosarcoma; oxidative stress; therapy; unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Breast Cancer: The Balance between Apoptosis and Autophagy and Its Role in Drug Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 16;20(4):857. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040857. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30781465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect and mechanisms of celastrol on the apoptosis of HOS osteosarcoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Oct;40(4):2260-2268. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6619. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30106429
-
A Systems Biological View of Life-and-Death Decision with Respect to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-The Role of PERK Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 5;18(1):58. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010058. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28067773 Free PMC article.
-
The active nuclear form of SREBP1 amplifies ER stress and autophagy via regulation of PERK.FEBS J. 2020 Jun;287(11):2348-2366. doi: 10.1111/febs.15144. Epub 2019 Dec 9. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 31736227
-
Oncogenic BRAF, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy: Crosstalk and therapeutic targets in cutaneous melanoma.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020 Jul-Sep;785:108321. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2020.108321. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32800272 Review.
Cited by
-
Delivery of miRNAs Using Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Osteosarcoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 22;19:8641-8660. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S471900. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39188861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered nanomaterials enhance drug delivery strategies for the treatment of osteosarcoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 21;14:1269224. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1269224. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37670948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism and senescence in the immune microenvironment of osteosarcoma: focus on new therapeutic strategies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 11;14:1217669. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1217669. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37497349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated single-cell analysis reveals heterogeneity and therapeutic insights in osteosarcoma.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 18;15(1):669. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01523-x. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39556142 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-related features predict the prognosis of osteosarcoma and reveal STC2 as a novel risk indicator for disease progression.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 25;14:1453173. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1453173. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39119088 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82060492/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- S202210403002/the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students in Jiangxi Province
- 202110403003/the National College Students' Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Plan Program
- 202210403001/the National College Students' Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Plan Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

