FTO promotes innate immunity by controlling NOD1 expression via m6A-YTHDF2 manner in teleost
- PMID: 36483010
- PMCID: PMC9722488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105646
FTO promotes innate immunity by controlling NOD1 expression via m6A-YTHDF2 manner in teleost
Abstract
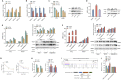
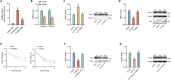
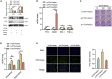
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant internal mRNA modification in eukaryotes, plays a vital role in regulating innate immunity. However, its underlying mechanism remains largely unknown, especially in lower vertebrates. The results of the present study show that fat-mass- and obesity-associated protein (FTO), also known as a m6A demethylase, improved the innate immunity and prevented Siniperca chuatsi rhabdo virus and Vibrio anguillarum infection in miiuy croaker. Significantly, FTO-promoted immunity was dependent on its m6A demethylase activity. In terms of mechanism, NOD1 has abundant methylation modification in its CDS and 3'UTR regions, and FTO can reduce its methylation level, thus avoiding its degradation by YTHDF2. In summary, our results indicate that the FTO-mediated m6A modification in NOD1 mRNA promotes innate immunity by activating the NOD-like receptor pathway, which provides a molecular mechanism for the regulation of immune response via RNA methylation in teleost.
Keywords: Epigenetics; immunology; transcriptomics.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
METTL3-Mediated m6A Modification of TRIF and MyD88 mRNAs Suppresses Innate Immunity in Teleost Fish, Miichthys miiuy.J Immunol. 2023 Jul 1;211(1):130-139. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300033. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37154684
-
m6A mRNA methylation controls autophagy and adipogenesis by targeting Atg5 and Atg7.Autophagy. 2020 Jul;16(7):1221-1235. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1659617. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31451060 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine demethyltransferase FTO-mediated autophagy in malignant development of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Oncogene. 2021 Jun;40(22):3885-3898. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01820-7. Epub 2021 May 10. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33972683
-
FTO m6A Demethylase in Obesity and Cancer: Implications and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 30;23(7):3800. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073800. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FTO in cancer: functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic implications.Trends Cancer. 2022 Jul;8(7):598-614. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2022.02.010. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Trends Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35346615 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights into transcriptome variation during cattle adipocyte adipogenesis by direct RNA sequencing.iScience. 2023 Aug 28;26(10):107753. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107753. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37692285 Free PMC article.
-
The GDF6-FTO axis modulates the innate immune and inflammatory response to human respiratory syncytial virus.iScience. 2024 Sep 26;27(10):111038. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111038. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39474078 Free PMC article.
-
An arms race between 5'ppp-RNA virus and its alternative recognition receptor MDA5 in RIG-I-lost teleost fish.Elife. 2024 Sep 30;13:RP94898. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94898. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39347580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shulman Z., Stern-Ginossar N. The RNA modification N-6-methyladenosine as a novel regulator of the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2020;21:501–512. - PubMed
-
- Dina C., Meyre D., Gallina S., Durand E., Körner A., Jacobson P., Carlsson L.M.S., Kiess W., Vatin V., Lecoeur C., et al. Variation in FTO contributes to childhood obesity and severe adult obesity. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:724–726. - PubMed
-
- Wang L., Wen M., Cao X. Nuclear hnRNPA2B1 initiates and amplifies the innate immune response to DNA viruses. Science. 2019;365:eaav0758. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

