Microalgae-Enabled Wastewater Remediation and Nutrient Recovery through Membrane Photobioreactors: Recent Achievements and Future Perspective
- PMID: 36363649
- PMCID: PMC9699475
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12111094
Microalgae-Enabled Wastewater Remediation and Nutrient Recovery through Membrane Photobioreactors: Recent Achievements and Future Perspective
Abstract
The use of microalgae for wastewater remediation and nutrient recovery answers the call for a circular bioeconomy, which involves waste resource utilization and ecosystem protection. The integration of microalgae cultivation and wastewater treatment has been proposed as a promising strategy to tackle the issues of water and energy source depletions. Specifically, microalgae-enabled wastewater treatment offers an opportunity to simultaneously implement wastewater remediation and valuable biomass production. As a versatile technology, membrane-based processes have been increasingly explored for the integration of microalgae-based wastewater remediation. This review provides a literature survey and discussion of recent progressions and achievements made in the development of membrane photobioreactors (MPBRs) for wastewater treatment and nutrient recovery. The opportunities of using microalgae-based wastewater treatment as an interesting option to manage effluents that contain high levels of nutrients are explored. The innovations made in the design of membrane photobioreactors and their performances are evaluated. The achievements pave a way for the effective and practical implementation of membrane technology in large-scale microalgae-enabled wastewater remediation and nutrient recovery processes.
Keywords: bioremediation; membrane photobioreactor; microalgae; nutrient recovery; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

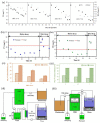
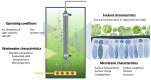

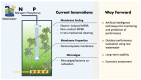
Similar articles
-
Membrane photobioreactors for integrated microalgae cultivation and nutrient remediation of membrane bioreactors effluent.Bioresour Technol. 2014 Jul;163:228-35. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.012. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Bioresour Technol. 2014. PMID: 24814249
-
Simultaneous removal of nutrient and sulfonamides from marine aquaculture wastewater by concentrated and attached cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris in an algal biofilm membrane photobioreactor (BF-MPBR).Sci Total Environ. 2020 Jul 10;725:138524. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138524. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32302854
-
Resource recovery from wastewaters using microalgae-based approaches: A circular bioeconomy perspective.Bioresour Technol. 2020 Apr;302:122817. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122817. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Bioresour Technol. 2020. PMID: 32007309 Review.
-
Resource recovery through bioremediation of wastewaters and waste carbon by microalgae: a circular bioeconomy approach.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Nov;28(42):58837-58856. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11645-8. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33527238 Review.
-
Improving membrane photobioreactor performance by reducing light path: operating conditions and key performance indicators.Water Res. 2020 Apr 1;172:115518. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115518. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Water Res. 2020. PMID: 31991292
Cited by
-
Membrane Technologies for Nitrogen Recovery from Waste Streams: Scientometrics and Technical Analysis.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;13(1):15. doi: 10.3390/membranes13010015. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36676822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Tiled Amplicon Sequencing Assay Targeting the Tomato Brown Rugose Fruit Virus (ToBRFV) Genome Reveals Widespread Distribution in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Systems in the Province of Ontario, Canada.Viruses. 2024 Mar 17;16(3):460. doi: 10.3390/v16030460. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543825 Free PMC article.
-
Wastewater treatment by algae-based membrane bioreactors: a review of the arrangement of a membrane reactor, physico-chemical properties, advantages and challenges.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 30;14(47):34769-34790. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04417g. eCollection 2024 Oct 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39483379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth Characteristics of a Desmodesmus Species from the San Antonio Springs and Its Short-Term Impact on Soil Microbial Dynamics.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;14(9):1053. doi: 10.3390/life14091053. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boretti A., Rosa L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. NPJ Clean Water. 2019;2:15. doi: 10.1038/s41545-019-0039-9. - DOI
-
- Poustie A., Yang Y., Verburg P., Pagilla K., Hanigan D. Reclaimed wastewater as a viable water source for agricultural irrigation: A review of food crop growth inhibition and promotion in the context of environmental change. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;739:139756. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139756. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Liu Y. Reverse osmosis concentrate: An essential link for closing loop of municipal wastewater reclamation towards urban sustainability. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;421 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127773. - DOI
-
- Wu H., Vaneeckhaute C. Nutrient recovery from wastewater: A review on the integrated Physicochemical technologies of ammonia stripping, adsorption and struvite precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;433:133664. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133664. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

