Epithelial cell alarmin cytokines: Frontline mediators of the asthma inflammatory response
- PMID: 36311787
- PMCID: PMC9616080
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.975914
Epithelial cell alarmin cytokines: Frontline mediators of the asthma inflammatory response
Abstract
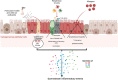
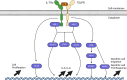
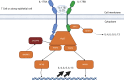
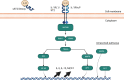
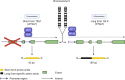
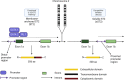
The exposure of the airway epithelium to external stimuli such as allergens, microbes, and air pollution triggers the release of the alarmin cytokines IL-25, IL-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). IL-25, IL-33 and TSLP interact with their ligands, IL-17RA, IL1RL1 and TSLPR respectively, expressed by hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells including dendritic cells, ILC2 cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. Alarmins play key roles in driving type 2-high, and to a lesser extent type 2-low responses, in asthma. In addition, studies in which each of these three alarmins were targeted in allergen-challenged mice showed decreased chronicity of type-2 driven disease. Consequently, ascertaining the mechanism of activity of these upstream mediators has implications for understanding the outcome of targeted therapies designed to counteract their activity and alleviate downstream type 2-high and low effector responses. Furthermore, identifying the factors which shift the balance between the elicitation of type 2-high, eosinophilic asthma and type-2 low, neutrophilic-positive/negative asthma by alarmins is essential. In support of these efforts, observations from the NAVIGATOR trial imply that targeting TSLP in patients with tezepelumab results in reduced asthma exacerbations, improved lung function and control of the disease. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms surrounding the secretion of IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP from the airway epithelium and how this influences the allergic airway cascade. We also review in detail how alarmin-receptor/co-receptor interactions modulate downstream allergic inflammation. Current strategies which target alarmins, their efficacy and inflammatory phenotype will be discussed.
Keywords: IL-25; IL-33; TSLP; allergy; tezepelumab.
Copyright © 2022 Duchesne, Okoye and Lacy.
Conflict of interest statement
PL reports grants from Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and Synergy Respiratory and Cardiac Care, and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline Canada, AstraZeneca Canada, and Synergy Respiratory and Cardiac Care, Canada, outside this submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Airway Epithelial-Derived Alarmins in Asthma: Perspectives for Therapeutic Targets.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 11;12(10):2312. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102312. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sounding the alarmins-The role of alarmin cytokines in asthma.Allergy. 2023 Feb;78(2):402-417. doi: 10.1111/all.15609. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Allergy. 2023. PMID: 36463491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-alarmin approaches entering clinical trials.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2020 Jan;26(1):69-76. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000615. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 31408015 Review.
-
The Role of Airway Epithelial Cell Alarmins in Asthma.Cells. 2022 Mar 24;11(7):1105. doi: 10.3390/cells11071105. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bronchial Allergen Challenge of Patients with Atopic Asthma Triggers an Alarmin (IL-33, TSLP, and IL-25) Response in the Airways Epithelium and Submucosa.J Immunol. 2018 Oct 15;201(8):2221-2231. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800709. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30185520
Cited by
-
Tyndallized bacteria prime bronchial epithelial cells to mount an effective innate immune response against infections.Hum Cell. 2024 Jul;37(4):1080-1090. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01080-z. Epub 2024 May 30. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38814518 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical respiratory sensitization-Current status of mechanistic understanding, knowledge gaps and possible identification methods of sensitizers.Front Toxicol. 2024 Jul 29;6:1331803. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2024.1331803. eCollection 2024. Front Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39135743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological factors, important players in the development of asthma.BMC Immunol. 2024 Jul 26;25(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12865-024-00644-w. BMC Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39060923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Airway Epithelial-Derived Alarmins in Asthma: Perspectives for Therapeutic Targets.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 11;12(10):2312. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102312. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiallergic Effects of Callerya atropurpurea Extract In Vitro and in an In Vivo Atopic Dermatitis Model.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;12(4):860. doi: 10.3390/plants12040860. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saunders KB. Origin of the word "asthma". Thorax. (1993) 48(6):646. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.6.647 - DOI

