A comprehensive analysis of the prognostic value and immune infiltration of low expression DBT in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36299888
- PMCID: PMC9589218
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1002588
A comprehensive analysis of the prognostic value and immune infiltration of low expression DBT in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
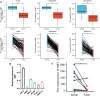
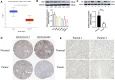
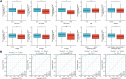
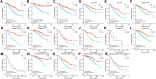
Background: Although DBT is strongly associated with human tumorigenesis and progression through a variety of pathways, the role of DBT in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has not been well established. Materials and methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) databset provides RNA sequencing data and clinicopathological information on ccRCC. The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database was used to validate the DBT expression levels, and qPCR was used to examine the DBT expression in renal cancer cell lines and ccRCC tissue samples from our centre. In parallel, DBT protein expression was explored in the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) database, and western blotting and immunohistochemistry of renal cancer cell lines and ccRCC tissues validated the results. Additionally, the diagnostic and prognostic value of DBT was comprehensively evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses, and Kaplan‒Meier survival analysis. The protein‒protein interaction (PPI) network based on the STRING website, Gene Ontology (GO) analysis, Kyoto Gene and Genome Encyclopedia (KEGG) analysis and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) further provided a landscape of the molecular mechanisms of DBT in ccRCC. Finally, the TIMER 2.0, GEPIA and TISIDB websites were used to understand the relationship between DBT and immune characteristics. Results: The mRNA expression and protein expression of DBT were significantly downregulated in ccRCC tissues relative to normal tissues, which was associated with poor clinical outcomes. DBT has an encouraging discriminatory power for ccRCC and is an independent prognostic factor for ccRCC patients. Mechanistically, DBT is mainly involved in the regulation of immune-related signalling pathways in ccRCC; it is associated with a variety of immune infiltrating cells and immune checkpoints. Conclusion: DBT is a tumour suppressor gene in ccRCC and could be used as a new biomarker for diagnostic and prognostic purposes, and it is associated with immune infiltration in ccRCC.
Keywords: DBT; bioInformatic; clear cell renal cell carcinoma; immune infiltration; prognostic biomarker.
Copyright © 2022 Xie, Xi, Liu, Zhang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A comprehensive analysis of MYO6 as a promising biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis, and immunity in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 31;12(8):2071-2098. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-227. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37701098 Free PMC article.
-
NUDT1 Could Be a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlated with Immune Infiltration in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Appl Bionics Biomech. 2022 Dec 26;2022:3669296. doi: 10.1155/2022/3669296. eCollection 2022. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2022. PMID: 36606241 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of gasdermin D in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its effect on its biological function.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 6;13:1163714. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1163714. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37483501 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on Immunotherapy and Immune Landscape in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;13(22):5856. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225856. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34831009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Prognostic Expression Markers for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 28;11:643065. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.643065. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33996558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic analysis of RNASET2 gene as a potential prognostic and immunological biomarker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2023 Sep 7;23(1):837. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11356-6. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37679715 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of novel genes related to immune microenvironment in polycystic ovary syndrome.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e40229. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040229. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470566 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of CENPM is associated with poor clinical outcome and suppression of immune profile in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Hereditas. 2023 Jan 13;160(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s41065-023-00262-3. Hereditas. 2023. PMID: 36635779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardolino M., Zingoni A., Cerboni C., Cecere F., Soriani A., Iannitto M. L., et al. (2011). DNAM-1 ligand expression on Ag-stimulated T lymphocytes is mediated by ROS-dependent activation of DNA-damage response: Relevance for NK-T cell interaction. Blood 117 (18), 4778–4786. 10.1182/blood-2010-08-300954 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cerboni C., Zingoni A., Cippitelli M., Piccoli M., Frati L., Santoni A. (2007). Antigen-activated human T lymphocytes express cell-surface NKG2D ligands via an ATM/ATR-dependent mechanism and become susceptible to autologous NK- cell lysis. Blood 110 (2), 606–615. 10.1182/blood-2006-10-052720 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

