Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
- PMID: 36289330
- PMCID: PMC9646526
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05366-w
Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
Abstract
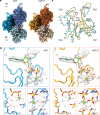
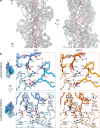
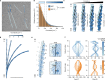
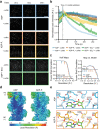
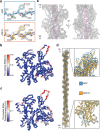
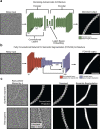
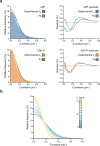
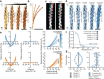
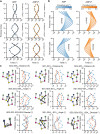
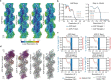
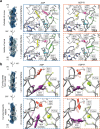
ATP-hydrolysis-coupled actin polymerization is a fundamental mechanism of cellular force generation1-3. In turn, force4,5 and actin filament (F-actin) nucleotide state6 regulate actin dynamics by tuning F-actin's engagement of actin-binding proteins through mechanisms that are unclear. Here we show that the nucleotide state of actin modulates F-actin structural transitions evoked by bending forces. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of ADP-F-actin and ADP-Pi-F-actin with sufficient resolution to visualize bound solvent reveal intersubunit interfaces bridged by water molecules that could mediate filament lattice flexibility. Despite extensive ordered solvent differences in the nucleotide cleft, these structures feature nearly identical lattices and essentially indistinguishable protein backbone conformations that are unlikely to be discriminable by actin-binding proteins. We next introduce a machine-learning-enabled pipeline for reconstructing bent filaments, enabling us to visualize both continuous structural variability and side-chain-level detail. Bent F-actin structures reveal rearrangements at intersubunit interfaces characterized by substantial alterations of helical twist and deformations in individual protomers, transitions that are distinct in ADP-F-actin and ADP-Pi-F-actin. This suggests that phosphate rigidifies actin subunits to alter the bending structural landscape of F-actin. As bending forces evoke nucleotide-state dependent conformational transitions of sufficient magnitude to be detected by actin-binding proteins, we propose that actin nucleotide state can serve as a co-regulator of F-actin mechanical regulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Catching actin proteins in action.Nature. 2022 Nov;611(7935):241-243. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-03343-x. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36289412 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Enabling Systemic Identification and Functionality Profiling for Cdc42 Homeostatic Modulators.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.05.574351. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.05.574351. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Chem. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):271. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01352-7. PMID: 38260445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Cofilin-Mediated Filament Softening and Crosslinking Counterbalance to Enhance Actin Network Flexibility.Phys Rev Lett. 2024 Nov 22;133(21):218402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.218402. Phys Rev Lett. 2024. PMID: 39642486
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Mechanisms of actin filament severing and elongation by formins.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8024):437-442. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07637-0. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38843827 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Helical reconstruction, again.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Apr;85:102788. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2024.102788. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38401399 Review.
-
The Shot CH1 domain recognises a distinct form of F-actin during Drosophila oocyte determination.Development. 2024 Apr 1;151(7):dev202370. doi: 10.1242/dev.202370. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Development. 2024. PMID: 38564309 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for subversion of host cell actin cytoskeleton during Salmonella infection.Sci Adv. 2023 Dec 8;9(49):eadj5777. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj5777. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38064550 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of inorganic-phosphate release from the core and barbed end of actin filaments.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Nov;30(11):1774-1785. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01101-9. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37749275 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the molecular mechanisms of actin cytoskeleton regulation in cell migration using cryo-EM.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Feb 27;51(1):87-99. doi: 10.1042/BST20220221. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36695514 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

