Investigation of market herbal products regulated under different categories: How can HPTLC help to detect quality problems?
- PMID: 36003516
- PMCID: PMC9393483
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.925298
Investigation of market herbal products regulated under different categories: How can HPTLC help to detect quality problems?
Abstract
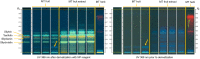
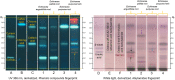
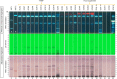
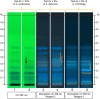
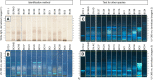
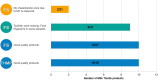
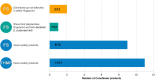
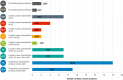
Background: Herbal products regulated under different categories were found to be of different quality. This has been demonstrated by the increasing number of reports on the quality of herbal products in the scientific literature. Proper identification is an effective way to address this concerning issue early on in a products' manufacturing process. Objectives: To assess the quality of milk thistle, coneflower and black cohosh herbal drugs, preparations and products commercialized under different regulatory categories, and to illustrate the usefulness of HPTLC as a tool for evaluating quality. Methods: HPTLC methods were adapted from the European Pharmacopeia's monographs for milk thistle fruits, black cohosh and purple coneflower. Additional detection modes beyond those described in the monographs were employed, and the entire HPTLC fingerprints were used for examination of identity and purity of the investigated samples. Results: All products regulated as Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products were shown to be of high quality: their fingerprints were consistent and without unexpected zones. A significant number of food supplements show quality issues (mainly adulterations): 52.4% of milk thistle, 33.3% of coneflower, and 45.5% of black cohosh products. The same was observed in 66.6% of black cohosh herbal drugs and preparations.
Keywords: HPTLC; THMP; black cohosh; coneflower; food supplement; milk thistle (Silybum marianum).
Copyright © 2022 Frommenwiler, Reich, Sharaf, Cañigueral and Etheridge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Detecting and Profiling of Milk Thistle Metabolites in Food Supplements: A Safety-Oriented Approach by Advanced Analytics.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 17;13(3):440. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030440. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of milk thistle (Silybum marianum) and black cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa) supplementation on digoxin pharmacokinetics in humans.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Jan;34(1):69-74. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.006312. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16221754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comprehensive HPTLC fingerprinting as a tool for a simplified analysis of purity of ginkgo products.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Oct 28;243:112084. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112084. Epub 2019 Jul 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31306695
-
United States Pharmacopeia review of the black cohosh case reports of hepatotoxicity.Menopause. 2008 Jul-Aug;15(4 Pt 1):628-38. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e31816054bf. Menopause. 2008. PMID: 18340277 Review.
-
Assessing the clinical significance of botanical supplementation on human cytochrome P450 3A activity: comparison of a milk thistle and black cohosh product to rifampin and clarithromycin.J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;46(2):201-13. doi: 10.1177/0091270005284854. J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16432272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Suitability of botanical extracts as components of complex mixtures used in herbal tea infusions-challenges and opportunities.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 7;13:1013340. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1013340. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36419619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detecting and Profiling of Milk Thistle Metabolites in Food Supplements: A Safety-Oriented Approach by Advanced Analytics.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 17;13(3):440. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030440. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984880 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blumenthal M., Goldberg A., Brinckmann J. (2000). Milk thistle fruit monograph. Herb. Med. Expand. Comm. E Monogr. 2000, 257–263.
-
- Cañigueral S., Arruda Frommenwiler D., Reich E., Vila R. (2018). “High performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) in the quality control of herbal products,” in Recent advances in pharmaceutical Sciences VIII. Editors Muñoz-Torrero D., Cajal Y., Llobet J. M. (Kerala: Research Signpost; ), 119–136.
-
- Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) European Medicines Agency (EMA) (2018b). European Union herbal monograph on Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. fructus. Amsterdam: European Medicines Agency, 1–7. EMA/HMPC/294187/2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

