PFKFB3 regulates cancer stemness through the hippo pathway in small cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 35804016
- PMCID: PMC9374593
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-022-02391-x
PFKFB3 regulates cancer stemness through the hippo pathway in small cell lung carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Correction to: PFKFB3 regulates cancer stemness through the hippo pathway in small cell lung carcinoma.Oncogene. 2023 Jan;42(1):79-82. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02470-z. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36443398 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
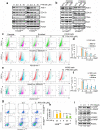
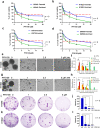
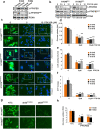
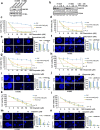
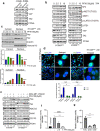
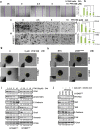
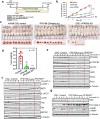
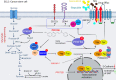
PFKFB3 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase) is the rate-limiting enzyme of glycolysis and is overexpressed in several human cancers that are associated with poor prognosis. High PFKFB3 expression in cancer stem cells promotes glycolysis and survival in the tumor microenvironment. Inhibition of PFKFB3 by the glycolytic inhibitor PFK158 and by shRNA stable knockdown in small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) cell lines inhibited glycolysis, proliferation, spheroid formation, and the expression of cancer stem cell markers CD133, Aldh1, CD44, Sox2, and ABCG2. These factors are also associated with chemotherapy resistance. We found that PFK158 treatment and PFKFB3 knockdown enhanced the ABCG2-interacting drugs doxorubicin, etoposide, and 5-fluorouracil in reducing cell viability under conditions of enriched cancer stem cells (CSC). Additionally, PFKFB3 inhibition attenuated the invasion/migration of SCLC cells by downregulating YAP/TAZ signaling while increasing pLATS1 via activation of pMST1 and NF2 and by reducing the mesenchymal protein expression. PFKFB3 knockdown and PFK158 treatment in a H1048 SCLC cancer stem cell-enriched mouse xenograft model showed significant reduction in tumor growth and weight with reduced expression of cancer stem cell markers, ABCG2, and YAP/TAZ. Our findings identify that PFKFB3 is a novel target to regulate cancer stem cells and its associated therapeutic resistance markers YAP/TAZ and ABCG2 in SCLC models.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DBO transitioned to postdoctoral training at AstraZeneca during this project. AstraZeneca was not involved in the funding, experimental design, and results of this manuscript. The authors declare no further competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PFKFB3 works on the FAK-STAT3-SOX2 axis to regulate the stemness in MPM.Br J Cancer. 2022 Oct;127(7):1352-1364. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01867-7. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Br J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35794237 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PFKFB3 induces cell death and synergistically enhances chemosensitivity in endometrial cancer.Oncogene. 2021 Feb;40(8):1409-1424. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01621-4. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33420377 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of PFKFB3 with a novel glycolytic inhibitor PFK158 promotes lipophagy and chemosensitivity in gynecologic cancers.Int J Cancer. 2019 Jan 1;144(1):178-189. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31868. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30226266 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment against glucose-dependent cancers through metabolic PFKFB3 targeting of glycolytic flux.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022 Jun;41(2):447-458. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10027-5. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022. PMID: 35419769 Review.
-
The role of PFKFB3 in maintaining colorectal cancer cell proliferation and stemness.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Oct;49(10):9877-9891. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07513-y. Epub 2022 May 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35553342 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the understanding of the role and mechanism of action of PFKFB3‑mediated glycolysis in liver fibrosis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Dec;54(6):105. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5429. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39301662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D cell culture models in research: applications to lung cancer pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 23;15:1438067. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1438067. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39376603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Continuous exposure to doxorubicin induces stem cell-like characteristics and plasticity in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells identified with the SORE6 reporter.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;94(4):571-583. doi: 10.1007/s00280-024-04701-4. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39180549 Free PMC article.
-
ALDH1: A potential therapeutic target for cancer stem cells in solid tumors.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 28;12:1026278. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1026278. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 drives thyroid cancer progression and lymph node metastasis by targeting LINC00894.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jan 30;24(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03240-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38291427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thirusangu P, Vigneshwaran V Lung cancer: pathophysiology and current advancements in therapeutics. In: Rayees S, Din I, Singh G, Malik FA (eds). Chronic Lung Diseases: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics. Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020, pp 129-41.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

