Improving quality of hepatitis B care in the Veteran's Health Administration
- PMID: 35795619
- PMCID: PMC9248930
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.1237
Improving quality of hepatitis B care in the Veteran's Health Administration
Abstract
Content available: Audio Recording.
Published 2022. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to report.
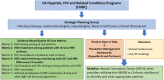
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insights Into Improving Outcomes for Post-Myocardial Infarction Veterans After Hospitalization at Veteran's Health Administration Versus Non-Veteran's Health Administration Hospitals.Med Care. 2024 Feb 1;62(2):69-71. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000001964. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Med Care. 2024. PMID: 38133571 No abstract available.
-
Poroid hidradenoma of the scalp in a US Veteran's Administration (VA) patient.Case Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2021 Jul 30;8(1):114-117. doi: 10.1080/23320885.2021.1956933. eCollection 2021. Case Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2021. PMID: 34377739 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of integrated care for elderly depressed patients in the PRISM-E study.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2009 Dec;12(4):205-13. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2009. PMID: 20195008
-
Measurement-Based Care in the Veteran's Health Administration: A Critique and Recommendations for Future Use in Mental Health Practice.J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2020 Dec;27(4):795-804. doi: 10.1007/s10880-019-09674-8. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2020. PMID: 31659593 Review.
-
The evolving role of advanced practice nursing within the new Veteran's Health Administration.Health Care Manage Rev. 1999 Fall;24(4):80-93. Health Care Manage Rev. 1999. PMID: 10572792 Review.
Cited by
-
Global epidemiology of cirrhosis - aetiology, trends and predictions.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Jun;20(6):388-398. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00759-2. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36977794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis delta testing trends in a US national cohort: An analysis of patient and provider-level predictive factors.Hepatol Commun. 2024 Apr 12;8(5):e0401. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000401. eCollection 2024 May 1. Hepatol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38619425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polaris Observatory Collaborators . Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:383–403. - PubMed

