Liver Stiffness on Magnetic Resonance Elastography and the MEFIB Index and Liver-Related Outcomes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participants
- PMID: 35788349
- PMCID: PMC9509452
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.073
Liver Stiffness on Magnetic Resonance Elastography and the MEFIB Index and Liver-Related Outcomes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participants
Abstract
Background & aims: Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is an accurate biomarker of liver fibrosis; however, limited data characterize its association with clinical outcomes. We conducted an individual participant data pooled meta-analysis on patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to evaluate the association between liver stiffness on MRE and liver-related outcomes.
Methods: A systematic search identified 6 cohorts of adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease who underwent a baseline MRE and were followed for hepatic decompensation, hepatocellular carcinoma, and death. Cox and logistic regression were used to assess the association between liver stiffness on MRE and liver-related outcomes, including a composite primary outcome defined as varices needing treatment, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy.
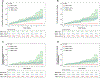
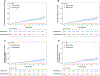
Results: This individual participant data pooled meta-analysis included 2018 patients (53% women) with a mean (± standard deviation) age of 57.8 (±14) years and MRE at baseline of 4.15 (±2.19) kPa, respectively. Among 1707 patients with available longitudinal data with a median (interquartile range) of 3 (4.2) years of follow-up, the hazard ratio for the primary outcome for MRE of 5 to 8 kPa was 11.0 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 7.03-17.1, P < .001) and for ≥ 8 kPa was 15.9 (95% CI: 9.32-27.2, P < .001), compared with those with MRE <5 kPa. The MEFIB index (defined as positive when MRE ≥3.3 kPa and Fibrosis-4 ≥1.6) had a robust association with the primary outcome with a hazard ratio of 20.6 (95% CI: 10.4-40.8, P < .001) and a negative MEFIB had a high negative predictive value for the primary outcome, 99.1% at 5 years. The 3-year risk of incident hepatocellular carcinoma was 0.35% for MRE <5 kPa, 5.25% for 5 to 8 kPa, and 5.66% for MRE ≥8 kPa, respectively.
Conclusion: Liver stiffness assessed by MRE is associated with liver-related events, and the combination of MRE and Fibrosis-4 has excellent negative predictive value for hepatic decompensation. These data have important implications for clinical practice.
Keywords: Ascites; Cirrhosis; Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; Portal Hypertension; Varices.
Copyright © 2022 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interests:
RL serves as a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Anylam/Regeneron, Amgen, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myer Squibb, CohBar, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gilead, Glympse bio, Hightide, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen Inc., Madrigal, Metacrine, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, Theratechnologies, 89 bio, Terns Pharmaceuticals and Viking Therapeutics. In addition his institutions received research grants from Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Astrazeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galectin Therapeutics, Galmed Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Intercept, Hanmi, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Merck, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sonic Incytes and Terns Pharmaceuticals. Co-founder of LipoNexus Inc.
Figures
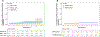
Comment in
-
Needle-free Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Prognostication: Moving One Step Closer.Gastroenterology. 2022 Oct;163(4):819-822. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.07.078. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 35944709 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
MR elastography-based liver fibrosis correlates with liver events in nonalcoholic fatty liver patients: A multicenter study.Liver Int. 2020 Sep;40(9):2242-2251. doi: 10.1111/liv.14593. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Liver Int. 2020. PMID: 32652744
-
Prognostic utility of magnetic resonance elastography and MEFIB index in predicting liver-related outcomes and mortality in individuals at risk of and with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 29;15:17562848221093869. doi: 10.1177/17562848221093869. eCollection 2022. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35509420 Free PMC article.
-
Low liver fat in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related significant fibrosis and cirrhosis is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma, decompensation and mortality.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Jan;59(1):80-88. doi: 10.1111/apt.17783. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 37968251 Free PMC article.
-
An individual patient data meta-analysis to determine cut-offs for and confounders of NAFLD-fibrosis staging with magnetic resonance elastography.J Hepatol. 2023 Sep;79(3):592-604. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.04.025. Epub 2023 Apr 29. J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37121437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;13(3):440-451.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.09.046. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25305349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in application of novel magnetic resonance imaging technologies in liver disease diagnosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul 28;29(28):4384-4396. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i28.4384. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37576700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of outcomes in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease based on initial measurements and subsequent changes in magnetic resonance elastography.J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan;59(1):56-65. doi: 10.1007/s00535-023-02049-9. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 37845417 Free PMC article.
-
Risk stratification and early detection biomarkers for precision HCC screening.Hepatology. 2023 Jul 1;78(1):319-362. doi: 10.1002/hep.32779. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Hepatology. 2023. PMID: 36082510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEFIB-Index and MAST-Score in the assessment of hepatic decompensation in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease-Individual participant data meta-analyses.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Nov;58(9):856-865. doi: 10.1111/apt.17707. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37694993 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Pathogenesis and Clinical Evaluation of Portal Hypertension in Chronic Liver Disease.Gut Liver. 2024 Jan 15;18(1):27-39. doi: 10.5009/gnl230072. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Gut Liver. 2024. PMID: 37842727 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016;64:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Loomba R, Wong R, Fraysse J, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression rates to cirrhosis and progression of cirrhosis to decompensation and mortality: a real world analysis of Medicare data. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;51:1149–1159. - PubMed
-
- Ekstedt M, Hagstrom H, Nasr P, et al. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology 2015;61:1547–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

