Liver Diseases in Latin America: Current Status, Unmet Needs, and Opportunities for Improvement
- PMID: 35729970
- PMCID: PMC9202671
- DOI: 10.1007/s11938-022-00382-1
Liver Diseases in Latin America: Current Status, Unmet Needs, and Opportunities for Improvement
Abstract
Purpose of review: To assess the current challenges regarding liver diseases, including the burden of disease, access to care, screening, and treatment needs in Latin America.
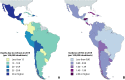
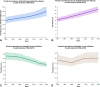
Recent findings: Latin America is a region with a rich multicultural heritage and important socioeconomic differences. The burden of liver diseases is high and mainly determined by a high level of alcohol intake and the surge of risk factors associated with NAFLD (i.e., sedentary lifestyles, broader access to highly processed foods, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus). Hepatotropic viruses also play a role in the development of chronic liver diseases, although their comparative frequency has been decreasing over the last decades. There are important disparities in access to screening and treatment for liver diseases in Latin America, which are reflected in low access to critical treatments such as direct-acting antiviral agents and drugs to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. Also, important barriers to liver transplantation are present in multiple countries, including a low deceased donors' rate and a lack of availability in several countries (especially in Central America). Our region also has disadvantages in research and education in liver diseases, which limits regional academic development and improvement in quality of care of liver diseases.
Summary: In order to tackle an increasing health burden due to liver diseases, Latin America urgently needs tailored interventions aiming to control the main risk factors for these disorders through the establishment of effective public health policies. Also, development of liver transplantation programs and improvement of medical education and research capabilities as well as extensive collaboration between all stakeholders are keys to address the liver disease agenda in the region.
Keywords: ALD; Alcohol; Alcohol use disorders; Alcohol-associated hepatitis; Cirrhosis; Fatty liver disease; Public policy; Steatosis.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestLuis Antonio Díaz declares that he has no conflict of interest. Gustavo Ayares declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jorge Arnold declares that he has no conflict of interest. Francisco Idalsoaga declares that he has no conflict of interest. Oscar Corsi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Marco Arrese declares that he has no conflict of interest. Juan Pablo Arab declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The burden of liver disease in Latin America.Ann Hepatol. 2024 May-Jun;29(3):101175. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2023.101175. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Ann Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 37922988 Review.
-
The 2023 Latin America report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: the imperative for health-centred climate-resilient development.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Apr 23;33:100746. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100746. eCollection 2024 May. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 38800647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NAFLD: Challenges and opportunities to address the public health problem in Latin America.Ann Hepatol. 2021 Sep-Oct;24:100359. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2021.100359. Epub 2021 May 15. Ann Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34004366
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Impact of Public Health Policies on Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease in Latin America: An Ecological Multinational Study.Hepatology. 2021 Nov;74(5):2478-2490. doi: 10.1002/hep.32016. Epub 2021 Aug 22. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 34134172
Cited by
-
Steatotic Donor Transplant Livers: Preservation Strategies to Mitigate against Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 24;25(9):4648. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094648. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copy Number Variation in the GSTM1 and GSTT1 Genes and the Risk of Liver Cirrhosis in Eastern Ethiopia.Appl Clin Genet. 2023 Oct 20;16:171-179. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S435852. eCollection 2023. Appl Clin Genet. 2023. PMID: 37881645 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of liver disease in Brazil, 1996-2022: a retrospective descriptive study of the epidemiology and impact on public healthcare.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Apr 19;33:100731. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100731. eCollection 2024 May. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 38800645 Free PMC article.
-
Global epidemiology of cirrhosis - aetiology, trends and predictions.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Jun;20(6):388-398. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00759-2. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36977794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HBV elimination in Central and South America: Current status and challenges.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2024 Jun 7;23(1):e0226. doi: 10.1097/CLD.0000000000000226. eCollection 2024 Jan-Jun. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38860128 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Bank Open Data. [cited 2022 Feb 21]; Available from: https://data.worldbank.org
-
- OECD. How’s Life in Latin America? Measuring well-being for policy making: Measuring well-being for policy making. OECD Publishing; 2021.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

