A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing
- PMID: 35539132
- PMCID: PMC9078458
- DOI: 10.1039/c7ra13510f
A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing
Abstract
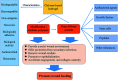
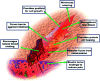
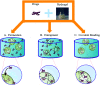
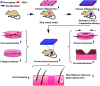
Functional active wound dressings are expected to provide a moist wound environment, offer protection from secondary infections, remove wound exudate and accelerate tissue regeneration, as well as to improve the efficiency of wound healing. Chitosan-based hydrogels are considered as ideal materials for enhancing wound healing owing to their biodegradable, biocompatible, non-toxic, antimicrobial, biologically adhesive, biological activity and hemostatic effects. Chitosan-based hydrogels have been demonstrated to promote wound healing at different wound healing stages, and also can alleviate the factors against wound healing (such as excessive inflammatory and chronic wound infection). The unique biological properties of a chitosan-based hydrogel enable it to serve as both a wound dressing and as a drug delivery system (DDS) to deliver antibacterial agents, growth factors, stem cells and so on, which could further accelerate wound healing. For various kinds of wounds, chitosan-based hydrogels are able to promote the effectiveness of wound healing by modifying or combining with other polymers, and carrying different types of active substances. In this review, we will take a close look at the application of chitosan-based hydrogels in wound dressings and DDS to enhance wound healing.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pullulan-Based Hydrogels in Wound Healing and Skin Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 4;24(5):4962. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054962. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan and Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wound Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 18;21(24):9656. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249656. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33352826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Inherently Antibacterial, Biodegradable, and Biologically Active Chitosan/Pseudo-Protein Hybrid Hydrogels as Biofunctional Wound Dressings.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Mar 31;13(12):14688-14699. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c21680. Epub 2021 Mar 19. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33739108
-
Controlled release of protein from gelatin/chitosan hydrogel containing platelet-rich fibrin encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles for accelerated wound healing in an animal model.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 15;225:588-604. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.117. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36403766
-
Tunicate-mimetic antibacterial hydrogel based on metal ion crosslinking and chitosan functionalization for wound healing.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jul 31;244:125062. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125062. Epub 2023 May 27. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37247717
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and Moisturizing Properties of Carboxymethyl Chitosan with Different Molecular Weights.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jun 28;12(7):1445. doi: 10.3390/polym12071445. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32605198 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of Biodegradable and Biocompatible Functional Polymers for Anti-Infection and Augmenting Wound Repair.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;15(1):120. doi: 10.3390/polym15010120. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell secretomes for wound healing and tissue regeneration: Next generation acellular based tissue engineered products.J Tissue Eng. 2022 Jul 28;13:20417314221114273. doi: 10.1177/20417314221114273. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2022. PMID: 35923177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric Oxide-Releasing Bacterial Cellulose/Chitosan Crosslinked Hydrogels for the Treatment of Polymicrobial Wound Infections.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 22;14(1):22. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010022. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056917 Free PMC article.
-
Hemostasis and Anti-Inflammatory Abilities of AuNPs-Coated Chitosan Dressing for Burn Wounds.J Pers Med. 2022 Jun 30;12(7):1089. doi: 10.3390/jpm12071089. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35887586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beanes S. R. Dang C. Soo C. Ting K. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2003;5:1–22. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

