The expanding universe of PARP1-mediated molecular and therapeutic mechanisms
- PMID: 35271815
- PMCID: PMC9232969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.02.021
The expanding universe of PARP1-mediated molecular and therapeutic mechanisms
Abstract
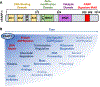
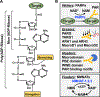
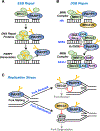
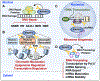
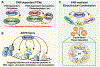
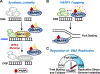
ADP-ribosylation (ADPRylation) is a post-translational modification of proteins catalyzed by ADP-ribosyl transferase (ART) enzymes, including nuclear PARPs (e.g., PARP1 and PARP2). Historically, studies of ADPRylation and PARPs have focused on DNA damage responses in cancers, but more recent studies elucidate diverse roles in a broader array of biological processes. Here, we summarize the expanding array of molecular mechanisms underlying the biological functions of nuclear PARPs with a focus on PARP1, the founding member of the family. This includes roles in DNA repair, chromatin regulation, gene expression, ribosome biogenesis, and RNA biology. We also present new concepts in PARP1-dependent regulation, including PAR-dependent post-translational modifications, "ADPR spray," and PAR-mediated biomolecular condensate formation. Moreover, we review advances in the therapeutic mechanisms of PARP inhibitors (PARPi) as well as the progress on the mechanisms of PARPi resistance. Collectively, the recent progress in the field has yielded new insights into the expanding universe of PARP1-mediated molecular and therapeutic mechanisms in a variety of biological processes.
Keywords: ADP-ribosylation; DNA damage response; DNA replication; PARP; PARP inhibitor; PARPi; PTM; RNA biology; biomolecular condensate; chromatin; gene regulation; histone; poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; post-translational modification; ribosome biogenesis; therapeutic resistance; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests W.L.K. is a founder of Ribon Therapeutics and a founder, consultant, and SAB member of ARase Therapeutics. He is also a co-holder of U.S. Patent 9,599,606 covering a set of ADP-ribose detection reagents, which have been licensed to and is sold by EMD Millipore. D.H. declares no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PARPs and ADP-ribosylation in RNA biology: from RNA expression and processing to protein translation and proteostasis.Genes Dev. 2020 Mar 1;34(5-6):302-320. doi: 10.1101/gad.334433.119. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32029452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MARTs and MARylation in the Cytosol: Biological Functions, Mechanisms of Action, and Therapeutic Potential.Cells. 2021 Feb 3;10(2):313. doi: 10.3390/cells10020313. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33546365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serine-linked PARP1 auto-modification controls PARP inhibitor response.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 1;12(1):4055. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24361-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34210965 Free PMC article.
-
The fast-growing business of Serine ADP-ribosylation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2022 Oct;118:103382. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2022.103382. Epub 2022 Jul 29. DNA Repair (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35963141 Review.
-
ADP-ribose hydrolases: biological functions and potential therapeutic targets.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Oct 8;26:e21. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.17. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39375922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the hepatoprotective potential of the parasitic plant Orobanche foetida Poir. aqueous extract against CCl4-induced liver injury in rat.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1320062. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1320062. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38239200 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "DNA Replication/Repair, and the DNA Damage Response in Human Disease".Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 11;14(4):893. doi: 10.3390/genes14040893. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107651 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted functions of DNA-PKcs: implications for the therapy of human diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jun 19;5(7):e613. doi: 10.1002/mco2.613. eCollection 2024 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38898995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP1 negatively regulates MAPK signaling by impairing BRAF-X1 translation.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Apr 3;16(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01428-2. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37013641 Free PMC article.
-
Alkylation of nucleobases by 2-chloro-N,N-diethylethanamine hydrochloride (CDEAH) sensitizes PARP1-deficient tumors.NAR Cancer. 2023 Aug 7;5(3):zcad042. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcad042. eCollection 2023 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37554969 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

