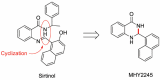
MHY2245, a Sirtuin Inhibitor, Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in HCT116 Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35163511
- PMCID: PMC8835956
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031590
MHY2245, a Sirtuin Inhibitor, Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in HCT116 Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
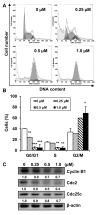
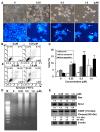
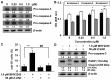
Sirtuins (SIRTs), which are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent class III histone deacetylases, regulate cell division, survival, and senescence. Although sirtinol, a synthetic SIRT inhibitor, is known to exhibit antitumor effects, its mechanism of action is not well understood. Therefore, we aimed to assess the anticancer effects and underlying mechanism of MHY2245, a derivative of sirtinol, in HCT116 human colorectal cancer cells in vitro. Treatment with MHY2245 decreased SIRT1 activity and caused DNA damage, leading to the upregulation of p53 acetylation, and increased levels of p53, phosphorylation of H2A histone family member X, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related kinase, checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1), and Chk2. The level of the breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein was also found to decrease. MHY2245 induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest via the downregulation of cyclin B1, cell division cycle protein 2 (Cdc2), and Cdc25c. Further, MHY2245 induced HCT116 cell death via apoptosis, which was accompanied by internucleosomal DNA fragmentation, decreased B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) levels, increased Bcl-2-asscociated X protein levels, cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, and activation of caspases -3, -8, and -9. Overall, MHY2245 induces cell cycle arrest, triggers apoptosis through caspase activation, and exhibits DNA damage response-associated anticancer effects.
Keywords: DNA damage response; SIRT inhibitor; apoptosis; cell cycle arrest; colorectal cancer cells; sirtinol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sirtinol, a class III HDAC inhibitor, induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2012 Sep;41(3):1101-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1534. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22751989
-
Gallic acid causes inactivating phosphorylation of cdc25A/cdc25C-cdc2 via ATM-Chk2 activation, leading to cell cycle arrest, and induces apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Dec;5(12):3294-302. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0483. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 17172433
-
MHY451 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by ROS generation in HCT116 human colorectal cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2017 Sep;38(3):1783-1789. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5836. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28731136
-
A new SIRT1 inhibitor, MHY2245, induces autophagy and inhibits energy metabolism via PKM2/mTOR pathway in human ovarian cancer cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Apr 6;16(11):1901-1916. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.44343. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32398958 Free PMC article.
-
A novel hydroxamic acid derivative, MHY218, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through downregulation of NF-κB in HCT116 human colon cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2014 Jan;44(1):256-64. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2163. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24190633
Cited by
-
Silencing GDI2 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer through activation of p53 signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 13;10(18):e37770. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37770. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39323841 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Chronic Degenerative Diseases: New Metabolic Targets in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 16;23(6):3212. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063212. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Components from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 19;24(3):1954. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031954. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin insights: bridging the gap between cellular processes and therapeutic applications.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Dec;397(12):9315-9344. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03263-9. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38976046 Review.
-
Mechanism of Resveratrol-Induced Programmed Cell Death and New Drug Discovery against Cancer: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13689. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213689. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

