Effectiveness and safety of combined therapy versus monotherapy based on immune checkpoint inhibitors and/or targeted drugs as salvage treatment for advanced urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35116530
- PMCID: PMC8797973
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-20-3354
Effectiveness and safety of combined therapy versus monotherapy based on immune checkpoint inhibitors and/or targeted drugs as salvage treatment for advanced urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The standard salvage regimen for the patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma (UC) is uncertain, although lots of novel agents are recommended, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and targeted drugs (TDs). We aimed to compare the effectiveness and safety of combined therapy of novel agents (CNA) and monotherapy of novel agents (MNA) as salvage therapy for advanced UC.
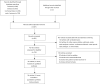
Methods: Studies exploring CNA and/or MNA for advanced UC in second-line setting were searched from PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science. The data of objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), median progression-free survival (PFS), median overall survival (OS), and grade 3-4 adverse effects rate (grade 3-4 AEs%) were pooled for analyses. Cochrane risk of bias tool was applied for the quality judgment of randomized controlled studies (RCTs).
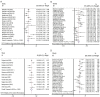
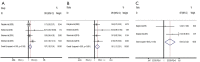
Results: Forty-one arms from 37 studies including 4,691 patients were included. Significant differences were presented in pooled ORR (22.9% versus 12.2%, OR =1.88, P<0.001) and DCR (62.7% versus 37.5%, OR =2.53, P<0.001) between CNA and MNA groups. The pooled median PFS was 3.66 months in CNA group versus 2.16 months in MNA group (WMD =1.50, P=0.028). No significant difference in pooled median OS was found between two groups (7.93 versus 7.50 months, WMD =0.43, P=0.449). 63.7% versus 25.4% of pooled grade 3-4 AEs% could be seen in CNA and MNA groups (OR =3.52, P<0.001). Additionally, the pooled results of PFS-6m and OS-6m in CNA group demonstrated significant advantages over MNA group (31.5% versus 28.7%, OR =1.31, P=0.049; 66.0% versus 56.7%, OR =1.34, P=0.029, respectively). In the subgroup analysis of CNA, use of ICIs, the positive expression of PD-L1 and ECOG-PS =0 were significantly associated with superior clinical outcomes (P<0.05).
Discussion: For advanced UC patients after first line agents, CNA had potential benefits than MNA in terms of ORR, DCR, median PFS, PFS-6m and OS-6m. However, CNA was associated with a significantly higher grade 3-4 AEs%. Furthermore, potential advantages were presented in CNA patients with ICIs usage, positive PD-L1 expression and ECOG-PS =0.
Keywords: Urothelial carcinoma (UC); combined therapy; monotherapy; novel agents; salvage therapy.
2021 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-20-3354). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Adv Ther. 2023 Feb;40(2):521-549. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02371-3. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 36399316
-
Second-line single-agent versus doublet chemotherapy as salvage therapy for metastatic urothelial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Oncol. 2016 Jan;27(1):49-61. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv509. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26487582 Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone as first-line therapy for advanced gastric and esophageal cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Dec;113(Pt A):109317. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109317. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36252494 Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of immunotherapy targeting the PD-1 pathway for advanced urothelial carcinoma: a meta-analysis of published clinical trials.Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 Oct;22(10):1750-1761. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02316-8. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32086783
-
Comparison of single agent versus combined chemotherapy in previously treated patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Mar 15;9:1535-43. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S97062. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27042121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, et al. Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:3068-77. 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.17.3068 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
