Emulating a target trial of the comparative effectiveness of clomiphene citrate and letrozole for ovulation induction
- PMID: 35048945
- PMCID: PMC8971650
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/deac005
Emulating a target trial of the comparative effectiveness of clomiphene citrate and letrozole for ovulation induction
Abstract
Study question: What are the comparative pregnancy outcomes in women who receive up to six consecutive cycles of ovulation induction with letrozole versus clomiphene citrate?
Summary answer: The risks of pregnancy, livebirth, multiple gestation, preterm birth, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admission and congenital malformations were higher for letrozole compared with clomiphene in participants with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), though no treatment differences were observed in those with unexplained infertility.
What is known already: Randomized trials have reported higher pregnancy and livebirth rates for letrozole versus clomiphene among individuals with PCOS, but no differences among those with unexplained infertility. None of these trials were designed to study maternal or neonatal complications.
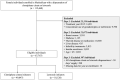
Study design, size, duration: We emulated a hypothetical trial of the comparative effectiveness of letrozole versus clomiphene citrate for ovulation induction among all women, then stratified by PCOS and unexplained infertility status. We used real-world data from a large healthcare claims database in the USA (2011-2015).
Participants/materials, setting, methods: We analyzed data from 18 120 women who initiated letrozole and 49 647 women who initiated clomiphene during 2011-2014, and who were aged 18-45 years with no history of diabetes, thyroid disease, liver disease or breast cancer and had no fertility treatments for 3 months before trial initiation. The treatment strategies were clomiphene citrate or letrozole for six consecutive cycles. The outcomes were pregnancy, livebirth, multiple gestation, preterm birth, small for gestational age (SGA), NICU admission and major congenital malformations. We estimated the probability of each outcome under each strategy via pooled logistic regression and used standardization to adjust for confounding and selection bias due to loss to follow-up.
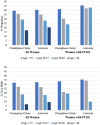
Main results and the role of chance: The estimated probabilities of pregnancy, livebirth and neonatal outcomes were similar under each strategy, both overall and among individuals with unexplained infertility. Among women with PCOS, the probability of pregnancy was 43% for letrozole vs 37% for clomiphene (risk difference [RD] = 6.0%; 95% CI: 4.4, 7.7) in the intention-to-treat analyses. The corresponding probability of livebirth was 32% vs 29% (RD = 3.1%; 95% CI: 1.5, 4.8). In per protocol analyses, the risk of multiple gestation was 19% vs 9%, the risk of preterm birth was 20% vs 15%, the risk of SGA was 5% vs 3%, the risk of NICU admission was 22% vs 16% and the risk of congenital malformation was 8% vs 2% among those with a livebirth.
Limitations, reasons for caution: We cannot completely rule out the possibility of residual confounding by body mass index or duration of infertility. However, we adjusted for proxies identified in administrative data and results did not change.
Wider implications of the findings: Our findings suggest that for women with unexplained infertility, the two treatments result in comparable probabilities of a livebirth. For women with PCOS, letrozole appears slightly more effective for attaining a livebirth. Neonatal outcomes were similar for the two treatments among women with unexplained infertility; we did not confirm the hypothesized higher risk of adverse neonatal outcomes for clomiphene versus letrozole. The risks of adverse neonatal outcomes were slightly greater among women with PCOS who were treated with letrozole versus clomiphene. It is likely that these effects are partially mediated through an increased risk of multiple gestation among women who received letrozole.
Study funding/competing interest(s): This work was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (R01HD088393). Y.-H.C. reports grants from the American Heart Association (834106) and NIH (R01HD097778). P.R. reports grants from the National Institutes of Health. J.H. reports grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the California Health Care Foundation during the conduct of the study; and consulting for several health care delivery organizations including Cambridge Health Alliance, Columbia University, University of Southern California, Community Servings, and the Delta Health Alliance. S.H.-D. reports grants from the National Institutes of Health and the US Food and Drug Administration during the conduct of the study; grants to her institution from Takeda outside the submitted work; consulting for UCB (biopharmaceutical company) and Roche; and being an adviser for the Antipsychotics Pregnancy Registry and epidemiologist for the North American Antiepileptics Pregnancy Registry, both at Massachusetts General Hospital. M.A.H. reports grants from the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Veterans Administration during the conduct of the study; being a consultant for Cytel; and being an adviser for ProPublica.
Trial registration number: N/A.
Keywords: clomiphene citrate; infertility; letrozole; ovulation induction; polycystic ovarian syndrome.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Double-blind randomized controlled trial of letrozole versus clomiphene citrate in subfertile women with polycystic ovarian syndrome.Hum Reprod. 2017 Aug 1;32(8):1631-1638. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex227. Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28854590 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fertility-related quality of life from two RCT cohorts with infertility: unexplained infertility and polycystic ovary syndrome.Hum Reprod. 2016 Oct;31(10):2268-79. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew175. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27402910 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Aromatase inhibitors (letrozole) for subfertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 24;5(5):CD010287. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010287.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 27;9:CD010287. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010287.pub4. PMID: 29797697 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
-
Aromatase inhibitors for subfertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 24;(2):CD010287. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010287.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 24;5:CD010287. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010287.pub3. PMID: 24563180 Updated. Review.
-
First-line ovulation induction for polycystic ovary syndrome: an individual participant data meta-analysis.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Nov 5;25(6):717-732. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz029. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31647106
Cited by
-
Comparison of Letrozole and Clomiphene Citrate in Pregnancy Outcomes in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Reprod Sci. 2024 Apr;31(4):883-905. doi: 10.1007/s43032-023-01404-8. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Reprod Sci. 2024. PMID: 38030814 Review.
-
Efficacy of Flavonoids on Animal Models of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 4;14(19):4128. doi: 10.3390/nu14194128. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Efficacy of Chinese Herbal Medicine in Animal Models of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 13;2022:4892215. doi: 10.1155/2022/4892215. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35996403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal Endometrial Receptivity and Oxidative Stress in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 25;13:904942. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.904942. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35959444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ovulation-induced frozen embryo transfer regimens in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Sep;41(9):2237-2251. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03209-3. Epub 2024 Jul 30. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 39080096 Review.
References
-
- Akbari Sene A, Ghorbani S, Ashrafi M.. Comparison of the pregnancy outcomes and the incidence of fetal congenital abnormalities in infertile women treated with letrozole and clomiphene citrate. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2018;44:1036–1041. - PubMed
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology. ACOG Practice Bulletin. Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists number 34, February 2002. Management of infertility caused by ovulatory dysfunction. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:347–358. - PubMed
-
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Evidence-based treatments for couples with unexplained infertility: a guideline. Fertil Steril 2020;113:305–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

