Bacterial two-component systems as sensors for synthetic biology applications
- PMID: 34917859
- PMCID: PMC8670732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coisb.2021.100398
Bacterial two-component systems as sensors for synthetic biology applications
Abstract
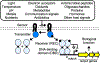
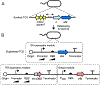
Two-component systems (TCSs) are a ubiquitous family of signal transduction pathways that enable bacteria to sense and respond to diverse physical, chemical, and biological stimuli outside and inside the cell. Synthetic biologists have begun to repurpose TCSs for applications in optogenetics, materials science, gut microbiome engineering, and soil nutrient biosensing, among others. New engineering methods including genetic refactoring, DNA-binding domain swapping, detection threshold tuning, and phosphorylation cross-talk insulation are being used to increase the reliability of TCS sensor performance and tailor TCS signaling properties to the requirements of specific applications. There is now potential to combine these methods with large-scale gene synthesis and laboratory screening to discover the inputs sensed by many uncharacterized TCSs and develop a large new family of genetically-encoded sensors that respond to an unrivaled breadth of stimuli.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rewiring bacterial two-component systems by modular DNA-binding domain swapping.Nat Chem Biol. 2019 Jul;15(7):690-698. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0286-6. Epub 2019 May 20. Nat Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31110305
-
Phosphatase activity tunes two-component system sensor detection threshold.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 12;9(1):1433. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03929-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29650958 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering transmembrane signal transduction in synthetic membranes using two-component systems.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 May 9;120(19):e2218610120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2218610120. Epub 2023 May 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37126679 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering two-component systems for advanced biosensing: From architecture to applications in biotechnology.Biotechnol Adv. 2024 Oct;75:108404. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108404. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Biotechnol Adv. 2024. PMID: 39002783 Review.
-
Engineering Whole-Cell Biosensors for Enhanced Detection of Environmental Antibiotics Using a Synthetic Biology Approach.Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Jun;64(2):402-408. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01259-w. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39010990 Review.
Cited by
-
Olfactory Receptors as an Emerging Chemical Sensing Scaffold.Biochemistry. 2023 Jan 17;62(2):187-195. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00486. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Biochemistry. 2023. PMID: 36318941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Reaction Models in Synthetic Promoter Design in Bacteria.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2844:3-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4063-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39068329
-
Strategies for Improving Small-Molecule Biosensors in Bacteria.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 25;12(2):64. doi: 10.3390/bios12020064. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35200325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in the two-component system's role in the synthesis of antibiotics by Streptomyces.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Aug;107(15):4727-4743. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12623-z. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37341754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in ligand-specific biosensing for structurally similar molecules.Cell Syst. 2023 Dec 20;14(12):1024-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2023.10.009. Cell Syst. 2023. PMID: 38128482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ni C, Dinh CV, Prather KLJ: Dynamic Control of Metabolism. Annu Rev Chem Biomol 2021, 12:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Boo A, Ellis T, Stan G-B: Host-Aware Synthetic Biology. Curr Opin Syst Biology 2019, 14:66–72.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
