Free fatty-acid transport via CD36 drives β-oxidation-mediated hematopoietic stem cell response to infection
- PMID: 34880245
- PMCID: PMC8655073
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27460-9
Free fatty-acid transport via CD36 drives β-oxidation-mediated hematopoietic stem cell response to infection
Abstract
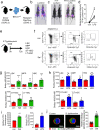
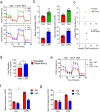
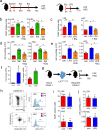
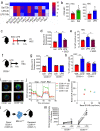
Acute infection is known to induce rapid expansion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), but the mechanisms supporting this expansion remain incomplete. Using mouse models, we show that inducible CD36 is required for free fatty acid uptake by HSCs during acute infection, allowing the metabolic transition from glycolysis towards β-oxidation. Mechanistically, high CD36 levels promote FFA uptake, which enables CPT1A to transport fatty acyl chains from the cytosol into the mitochondria. Without CD36-mediated FFA uptake, the HSCs are unable to enter the cell cycle, subsequently enhancing mortality in response to bacterial infection. These findings enhance our understanding of HSC metabolism in the bone marrow microenvironment, which supports the expansion of HSCs during pathogenic challenge.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ROS-mediated PI3K activation drives mitochondrial transfer from stromal cells to hematopoietic stem cells in response to infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 3;116(49):24610-24619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913278116. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31727843 Free PMC article.
-
A new leptin-mediated mechanism for stimulating fatty acid oxidation: a pivotal role for sarcolemmal FAT/CD36.Biochem J. 2017 Jan 1;474(1):149-162. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160804. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 27827305
-
Fatty acid oxidation in cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondria is unaffected by deletion of CD36.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007 Nov 15;467(2):234-8. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2007.08.020. Epub 2007 Aug 29. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007. PMID: 17904092 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise- and training-induced upregulation of skeletal muscle fatty acid oxidation are not solely dependent on mitochondrial machinery and biogenesis.J Physiol. 2013 Sep 15;591(18):4415-26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.238451. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 22890711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD36: The Bridge between Lipids and Tumors.Molecules. 2024 Jan 21;29(2):531. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020531. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38276607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD36 cell surface expression as a surrogate marker to identify ABL/JAK-class kinase fusions in pediatric BCP-ALL.Leukemia. 2025 Jan;39(1):64-74. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02421-5. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 39420220
-
In Vivo Imaging of Bone Marrow Long-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2675:43-49. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3247-5_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37258754
-
Docosahexaenoic Acid Counteracts the Hypoxic-Induced Inflammatory and Metabolic Alterations in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 1;14(21):4600. doi: 10.3390/nu14214600. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364860 Free PMC article.
-
Diarrhea induced by insufficient fat absorption in weaned piglets: Causes and nutrition regulation.Anim Nutr. 2023 Dec 27;16:299-305. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.12.004. eCollection 2024 Mar. Anim Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38371473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
You are what you eat: How to best fuel your immune system.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 20;13:1003006. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1003006. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36211413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

