TRPA1 promotes cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through inflammation mediated by the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 34790784
- PMCID: PMC8576655
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-5125
TRPA1 promotes cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through inflammation mediated by the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: The nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin (DDP) has been a severe obstacle for its clinical use in anticancer treatment. The apoptosis and inflammation induced by DDP are the main causes of the nephrotoxicity. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) is a non-selective cation ligand-gated channel that is involved in the inflammation progress.
Methods: The apoptosis, inflammation, MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway, and TRPA1 expression were assessed after HEK293 cells had been induced by DDP, and the role of TRPA1 in apoptosis and inflammation of DDP-induced HEK293 cells treated with TRPA1 antagonist HC-030031 was also evaluated by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), flow cytometry, and western blot assays.
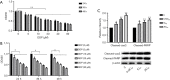
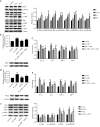
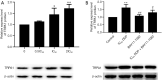
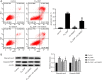
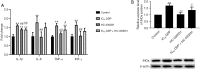
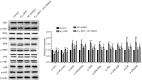
Results: The cell viability was reduced by DDP in both a time-dependent and dose-dependent manner with a minimal cytotoxic concentration of 10 μM. Moreover, DDP induced an enhancement of the apoptosis and inflammation in a dose-dependent manner, as indicated by the increase of the relative protein level of cleaved-caspase3 (cleaved-cas3), the cleavage product of caspase-3 substrate poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (cleaved-PARP) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression level of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interferon-γ (INF-γ). Additionally, DDP treatment increased the protein phosphorylation expression of IKKβ, JNK, ERK, and p38 in a dose-dependent manner, which was antagonized by the treatment of NF-κB-specific inhibitor BAY 11-7082 and pan-MAPK inhibitor U0126. It was also found that DDP upregulated the expression of TRPA1 at both the mRNA and protein levels in a dose-dependent manner. Besides, block of TRPA1 with HC-030031 relieved the apoptosis, diminished the level of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and INF-γ, reduced the level of cleaved-cas3, cleaved-PARP, and iNOS, decreased the p-IKKβ, p-JNK, p-ERK, and p-p38 expression, and enhanced the expression of IκBα.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results indicate that TRPA1 regulates DDP-induced nephrotoxicity via inflammation mediated by the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in HEK293 cells.
Keywords: Cisplatin (DDP); MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway; apoptosis; nephrotoxicity; transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1).
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-5125). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
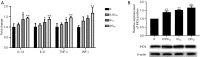
Similar articles
-
Saikosaponin-D reduces cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by repressing ROS-mediated activation of MAPK and NF-κB signalling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Sep;28(1):399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.06.020. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26118633
-
Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 mediates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in renal tubular cells via calcium-dependent signaling pathway.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Aug;10(8):9025-9038. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1867. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34488389
-
[miR-155-5p alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells by down-regulating SOCS1].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Mar;39(3):220-229. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36946346 Chinese.
-
Curcumin treatment attenuates cisplatin-induced gastric mucosal inflammation and apoptosis through the NF- κ B and MAPKs signaling pathway.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271221128738. doi: 10.1177/09603271221128738. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36178099
-
α-Bisabolol Attenuates Doxorubicin Induced Renal Toxicity by Modulating NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 10;23(18):10528. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810528. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142441 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
TRPA1 promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via regulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mitochondrial damage.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 5;21(1):695. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04351-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37798747 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on the Regulatory Action of TRP Channels: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Nociceptive Pain.Neurosci Insights. 2023 Dec 24;18:26331055231220340. doi: 10.1177/26331055231220340. eCollection 2023. Neurosci Insights. 2023. PMID: 38146332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of the effects of solid lipid nanoparticles of ivermectin and ivermectin on cuprizone-induced demyelination via targeting the TRPA1/NF-kB/GFAP signaling pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(11):1272-1282. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.71309.15493. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37886003 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on TRPA1 in Diseases.J Membr Biol. 2023 Dec;256(4-6):301-316. doi: 10.1007/s00232-023-00277-x. Epub 2023 Apr 11. J Membr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37039840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jul 5;8(1):261. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01464-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37402746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
