Changes of Intestinal Flora and Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure
- PMID: 34764999
- PMCID: PMC8577924
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/4288739
Changes of Intestinal Flora and Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Changes of Intestinal Flora and Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9898674. doi: 10.1155/2023/9898674. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38125188 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the changes of intestinal flora and lymphocyte subsets in patients with chronic renal failure (CRF).
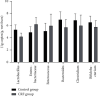
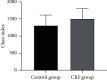
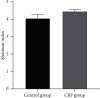
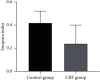
Methods: 60 CRF patients who were treated from June 2018 to June 2019 were selected; 60 healthy persons were selected as the control group. 16S rDNA was used to detect the expression of Lactobacillus, Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus, Bacteroides, Clostridium, and Bifidobacterium in the feces of the two groups. Illumina Miseq sequencing (Solexa sequencing technology) method was used to analyze the structural differences and species diversity of intestinal flora, including species richness index (Chao) and diversity index (Shannon, Simpson). Flow cytometry was used to detect the levels of lymphocytes and their subgroups of the two groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between Chao and lymphocyte subsets.
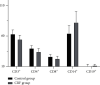
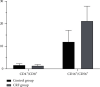
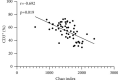
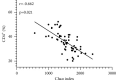
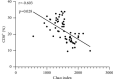
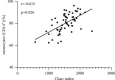
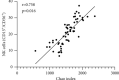
Results: The number of Enterobacteriaceae and Enterococcus in CRF group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05), while the Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Clostridium, and Bifidobacterium were opposite (P < 0.05). The Simpson index of the CRF group was lower than that of the control group, while the Chao index and Shannon index were opposite (P < 0.05). The levels of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+ in the CRF group were lower than those in the control group, while the levels of CD14+, CD19+, and CD16+/CD56+ were opposite (P < 0.05). The intestinal flora Chao index of CRF group was negatively correlated with the levels of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ (r = -0.692, P=0.019; r = -0.669, P=0.021; r = -0.603, P=0.028). The intestinal flora Chao of CRF group is positively correlated with the level of CD14+ and CD16+/CD56+ (r = 0.615, P=0.026; r = 0.758, P=0.016).
Conclusion: There are intestinal flora disorder and the imbalance of immune function in CRF patients, which are mainly manifested in the change of intestinal flora structure, the increase of richness and diversity of intestinal flora, and the decrease of lymphocyte subgroups. There is correlation between the imbalance of intestinal colony and the imbalance of immune function.
Copyright © 2021 Yan Lv et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Correlation study between changes in intestinal microflora structure and immune indexes in newly treated patients with pulmonary tuberculosis].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Dec 6;55(12):1486-1490. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20210728-00721. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34963248 Chinese.
-
A Study of the Relationship between Inflammatory Immune Function and Intestinal Flora in Adolescent Patients with First-Episode Depression.Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2024 Feb;52(1):1-9. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2024. PMID: 38454896 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Intestinal Flora From Chronic Renal Failure Complicated With Coronary Heart Disease and its Correlation With Arterial Stiffness Index.Altern Ther Health Med. 2023 Jan;29(1):252-257. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023. PMID: 36350321
-
[Detection and analysis of intestinal flora diversity in patients with complex anal fistula].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Sep 25;25(9):792-797. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20220412-00142. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36117370 Chinese.
-
Effects of Bifidobacterium bifidum tetragonum tablets and Jin Gui Ren Qi Pill on intestinal flora and metabolism in patients with diabetic kidney disease.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 29;15:1346168. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1346168. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39139646 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A cross-sectional study on gut microbiota in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing kidney transplant or hemodialysis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Mar 15;15(3):1756-1765. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37056836 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Multimedia Health Education on Psychological Burden, Quality of Life Ability, and Self-Efficacy of Congenital Microtia.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 11;2022:1482865. doi: 10.1155/2022/1482865. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35991152 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Changes of Intestinal Flora and Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9898674. doi: 10.1155/2023/9898674. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38125188 Free PMC article.
-
The antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects of FZHY prescription on the kidney in rats after unilateral ureteral obstruction.Acta Cir Bras. 2023 Jan 6;37(10):e371003. doi: 10.1590/acb371003. eCollection 2023. Acta Cir Bras. 2023. PMID: 36629622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stevens P. E., Levin A., Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group Members Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Annals of Internal Medicine . 2013;158(11):825–830. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-11-201306040-00007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

