Tea polyphenol modified, photothermal responsive and ROS generative black phosphorus quantum dots as nanoplatforms for promoting MRSA infected wounds healing in diabetic rats
- PMID: 34758829
- PMCID: PMC8579683
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-01106-w
Tea polyphenol modified, photothermal responsive and ROS generative black phosphorus quantum dots as nanoplatforms for promoting MRSA infected wounds healing in diabetic rats
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Tea polyphenol modified, photothermal responsive and ROS generative black phosphorus quantum dots as nanoplatforms for promoting MRSA infected wounds healing in diabetic rats.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Apr 19;20(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01408-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35439993 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Healing of MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) infected deep burn wounds (MIDBW) in diabetic patients remains an obstacle but is a cutting-edge research problem in clinical science. Surgical debridement and continuous antibiotic use remain the primary clinical treatment for MIDBW. However, suboptimal pharmacokinetics and high doses of antibiotics often cause serious side effects such as fatal complications of drug-resistant bacterial infections. MRSA, which causes wound infection, is currently a bacterium of concern in diabetic wound healing. In more severe cases, it can even lead to amputation of the patient's limb. The development of bioactive nanomaterials that can promote infected wound healing is significant.
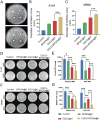
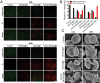
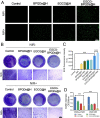
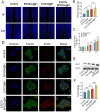
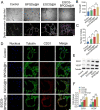
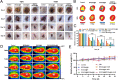
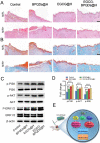
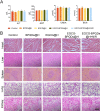
Results: The present work proposed a strategy of using EGCG (Epigallocatechin gallate) modified black phosphorus quantum dots (BPQDs) as therapeutic nanoplatforms for MIDBW to achieve the synergistic functions of NIR (near-infrared)-response, ROS-generation, sterilization, and promoting wound healing. The electron spin resonance results revealed that EGCG-BPQDs@H had a more vital photocatalytic ability to produce singlet oxygen than BPQDs@H. The inhibition results indicated an effective bactericidal rate of 88.6% against MRSA. Molecular biology analysis demonstrated that EGCG-BPQDs significantly upregulated CD31 nearly fourfold and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) nearly twofold, which were beneficial for promoting the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells and skin epidermal cells. Under NIR irradiation, EGCG-BPQDs hydrogel (EGCG-BPQDs@H) treated MIDBW area could rapidly raise temperature up to 55 °C for sterilization. The MIBDW closure rate of rats after 21 days of treatment was 92.4%, much better than that of 61.1% of the control group. The engineered EGCG-BPQDs@H were found to promote MIDBW healing by triggering the PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways, which could enhance cell proliferation and differentiation. In addition, intravenous circulation experiment showed good biocompatibility of EGCG-BPQDs@H. No significant damage to major organs was observed in rats.
Conclusions: The obtained results demonstrated that EGCG-BPQDs@H achieved the synergistic functions of photocatalytic property, photothermal effects and promoted wound healing, and are promising multifunctional nanoplatforms for MIDBW healing in diabetics.
Keywords: Black phosphorus quantum dots; Diabetic deep-burn wound healing; Multifunctional nanoplatforms; Photocatalytic; Photothermal.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preparation of NIR-responsive, ROS-generating and antibacterial black phosphorus quantum dots for promoting the MRSA-infected wound healing in diabetic rats.Acta Biomater. 2022 Jan 1;137:199-217. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Oct 10. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 34644613
-
Encapsulation of green tea polyphenol nanospheres in PVA/alginate hydrogel for promoting wound healing of diabetic rats by regulating PI3K/AKT pathway.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 May;110:110686. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110686. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32204114
-
An NIR-Triggered Au Nanocage Used for Photo-Thermo Therapy of Chronic Wound in Diabetic Rats Through Bacterial Membrane Destruction and Skin Cell Mitochondrial Protection.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 30;12:779944. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.779944. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34925036 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Cancer Research: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2024 Jul 15;382(3):25. doi: 10.1007/s41061-024-00470-z. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2024. PMID: 39009867 Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Green Tea EGCG on Skin Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2021 Oct 11;26(20):6123. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206123. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684703 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthetic selenium nanoparticles as co-adjuvant improved immune responses against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 19;39(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03455-6. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36401129 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial metal nanoclusters.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jul 16;20(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01538-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35842693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graphene Oxide/Black Phosphorus Functionalized Collagen Scaffolds with Enhanced Near-Infrared Controlled In Situ Biomineralization for Promoting Infectious Bone Defect Repair through PI3K/Akt Pathway.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Sep 25;16(38):50369-50388. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c10284. Epub 2024 Sep 12. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39264653
-
Hyaluronidase-Responsive Bactericidal Cryogel for Promoting Healing of Infected Wounds: Inflammatory Attenuation, ROS Scavenging, and Immune Regulation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 May;11(17):e2306602. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306602. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38350733 Free PMC article.
-
ADSC-exo@MMP-PEG smart hydrogel promotes diabetic wound healing by optimizing cellular functions and relieving oxidative stress.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Jul 16;16:100365. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100365. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35967739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao B, Xiao F, Xing D, et al. Polyprodrug antimicrobials: remarkable membrane damage and concurrent drug release to combat antibiotic resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Small. 2018;14(41):1802008. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Zhang X, Liu C, et al. Biologically modified nanoparticles as theranostic bionanomaterials. Progr Mater Sci. 2020;1:100768.
-
- Chen S, Zhang S, Galluzzi M, et al. Insight into multifunctional polyester fabrics finished by one-step eco-friendly strategy. Chem Eng J. 2019;358:634–642.
-
- Dang CN, Prasad YDM, Boulton AJM, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the diabetic foot clinic: a worsening problem. Diabet Med. 2003;20(2):159–161. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

